Question 166
DRAG DROP
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question on this series.
You have a database that tracks orders and deliveries for customers in North America. System versioning is enabled for all tables. The database contains the Sales.Customers, Application.Cities, and Sales.CustomerCategories tables.
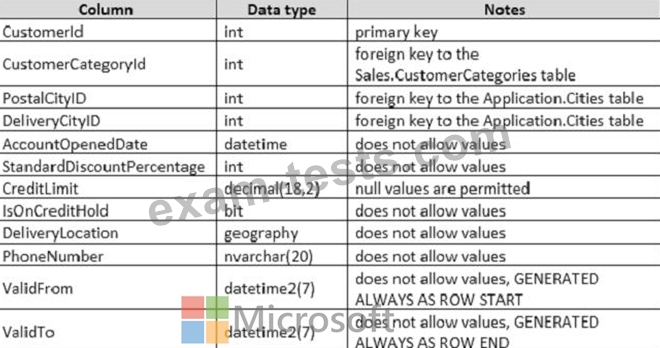
Details for the Sales.Customers table are shown in the following table:
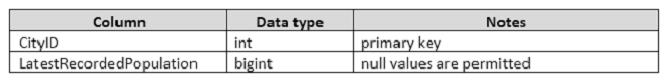
Details for the Application.Cities table are shown in the following table:
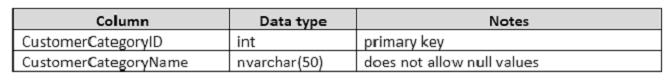
Details for the Sales.CustomerCategories table are shown in the following table:
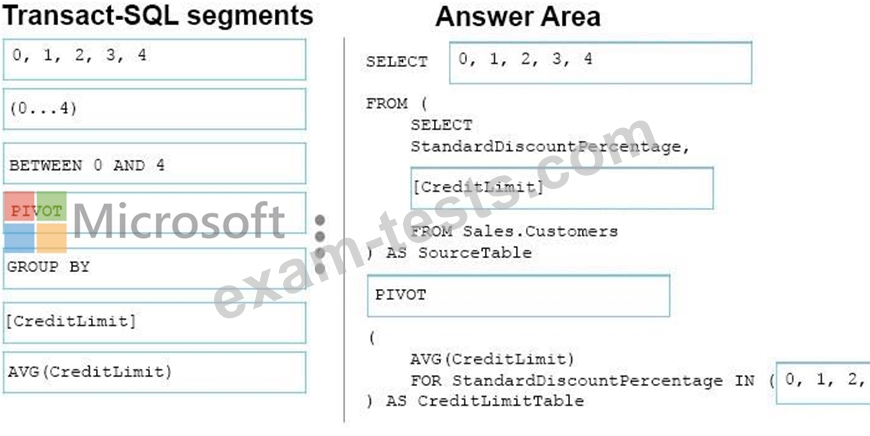
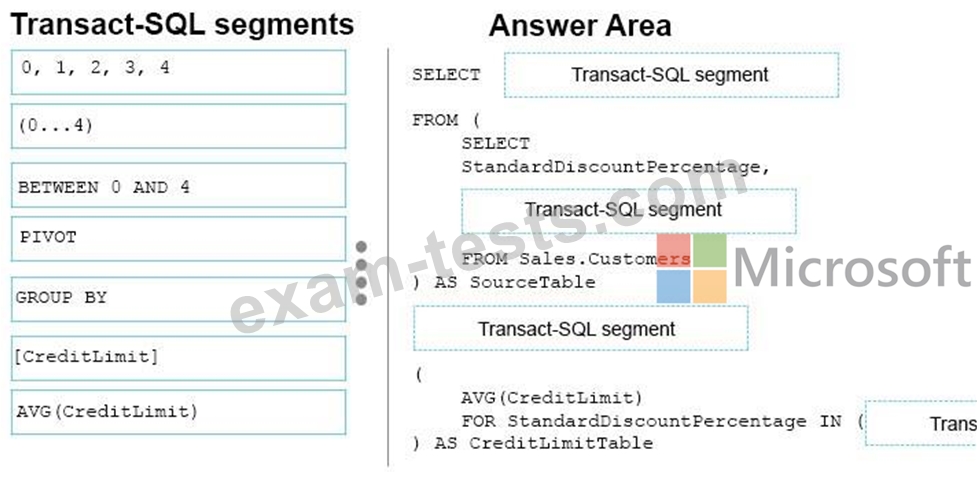
The marketing department is performing an analysis of how discount affect credit limits. They need to know the average credit limit per standard discount percentage for customers whose standard discount percentage is between zero and four.
You need to create a query that returns the data for the analysis.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL segments to the correct locations. Each Transact-SQL segments may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question on this series.
You have a database that tracks orders and deliveries for customers in North America. System versioning is enabled for all tables. The database contains the Sales.Customers, Application.Cities, and Sales.CustomerCategories tables.
Details for the Sales.Customers table are shown in the following table:

Details for the Application.Cities table are shown in the following table:

Details for the Sales.CustomerCategories table are shown in the following table:

The marketing department is performing an analysis of how discount affect credit limits. They need to know the average credit limit per standard discount percentage for customers whose standard discount percentage is between zero and four.
You need to create a query that returns the data for the analysis.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL segments to the correct locations. Each Transact-SQL segments may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:

Question 167
You create a table named Sales.Categories by running the following Transact-SQL statement:

You add the following data to the table.
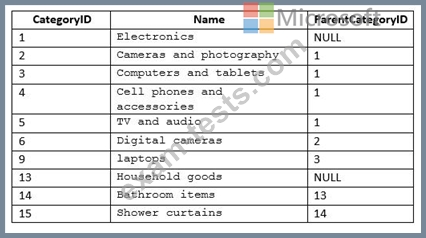
You need to create a query that uses a common table expression (CTE) to show the parent category of each category. The query must meet the following requirements:
Return all columns from the Categories table in the order shown.
Exclude all categories that do not have a parent category.
Construct the query using the following guidelines:
Name the expression ParentCategories.
Use PC as the alias for the expression.
Use C as the alias for the Categories table.
Use the AS keyword for all table aliases.
Use individual column names for each column that the query returns.
Do not use a prefix for any column name.
Do not surround object names with square brackets.
Part of the correct Transact-SQL has been provided in the answer area below. Enter the code in the answer area that resolves the problem and meets the stated goals or requirements. You can add code within the code that has been provided as well as below it.

Use the Check Syntax button to verify your work. Any syntax or spelling errors will be reported by line and character position. You may check syntax as many times as needed.

You add the following data to the table.

You need to create a query that uses a common table expression (CTE) to show the parent category of each category. The query must meet the following requirements:
Return all columns from the Categories table in the order shown.
Exclude all categories that do not have a parent category.
Construct the query using the following guidelines:
Name the expression ParentCategories.
Use PC as the alias for the expression.
Use C as the alias for the Categories table.
Use the AS keyword for all table aliases.
Use individual column names for each column that the query returns.
Do not use a prefix for any column name.
Do not surround object names with square brackets.

Part of the correct Transact-SQL has been provided in the answer area below. Enter the code in the answer area that resolves the problem and meets the stated goals or requirements. You can add code within the code that has been provided as well as below it.

Use the Check Syntax button to verify your work. Any syntax or spelling errors will be reported by line and character position. You may check syntax as many times as needed.
Question 168
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply to that question.
You have a database for a banking system. The database has two tables named tblDepositAcct and tblLoanAcct that store deposit and loan accounts, respectively. Both tables contain the following columns:
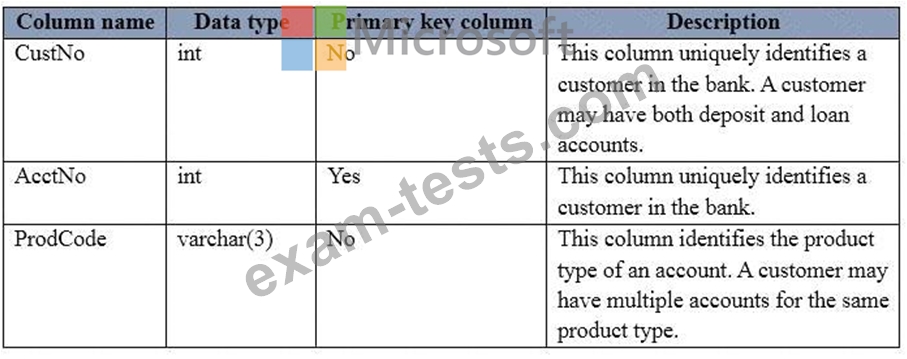
You need to determine the total number of deposit and loan accounts.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run?
You have a database for a banking system. The database has two tables named tblDepositAcct and tblLoanAcct that store deposit and loan accounts, respectively. Both tables contain the following columns:

You need to determine the total number of deposit and loan accounts.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run?
Question 169
DRAG DROP
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
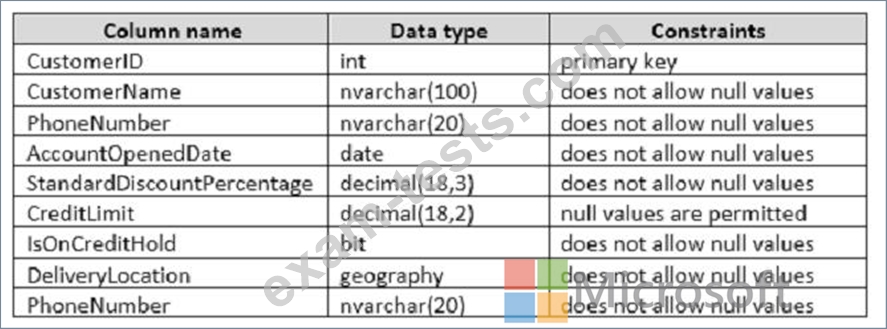
You are developing a database to track customer orders. The database contains the following tables:
Sales.Customers, Sales.Orders, and Sales.OrderLines. The following table describes the columns in Sales.Customers.
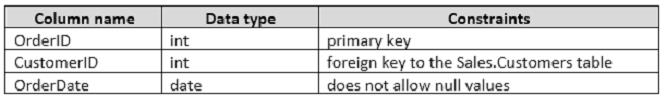
The following table describes the columns in Sales.Orders.
The following table describes the columns in Sales.OrderLines.

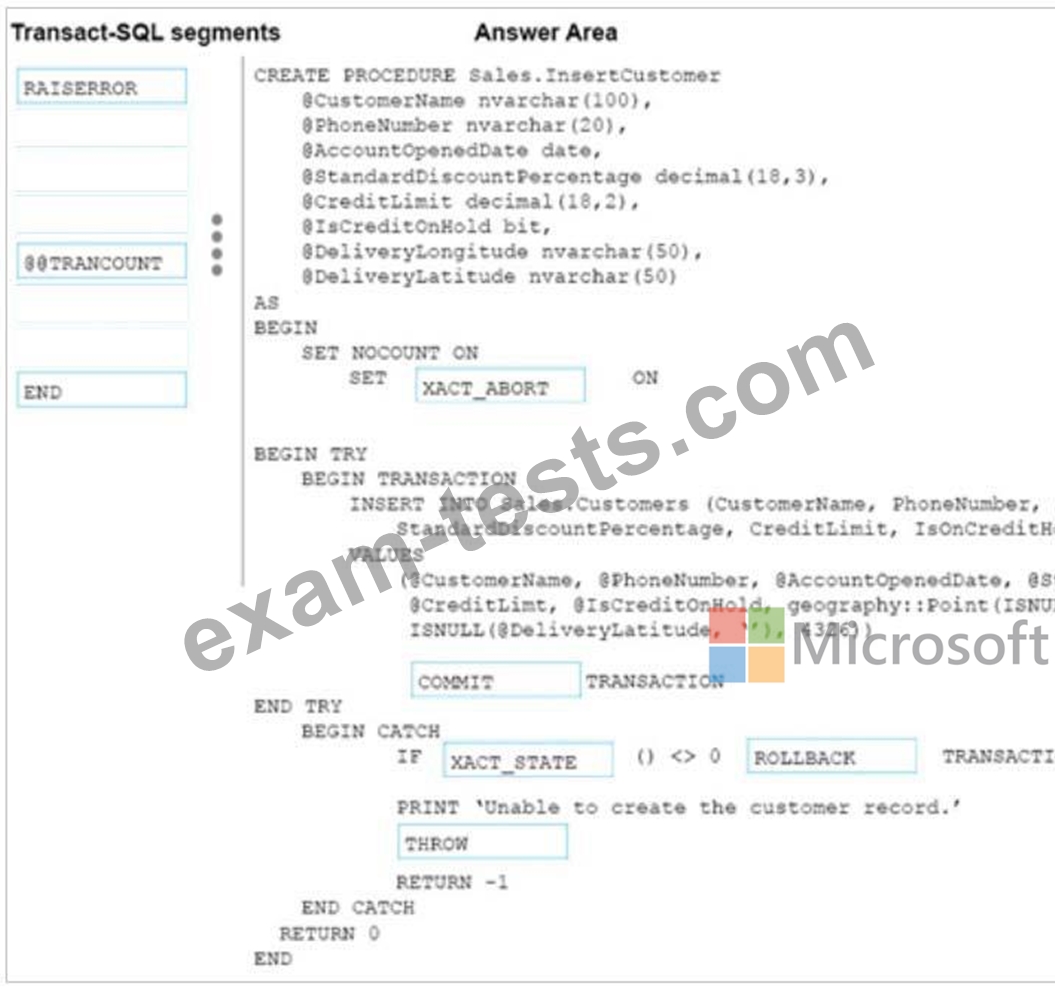
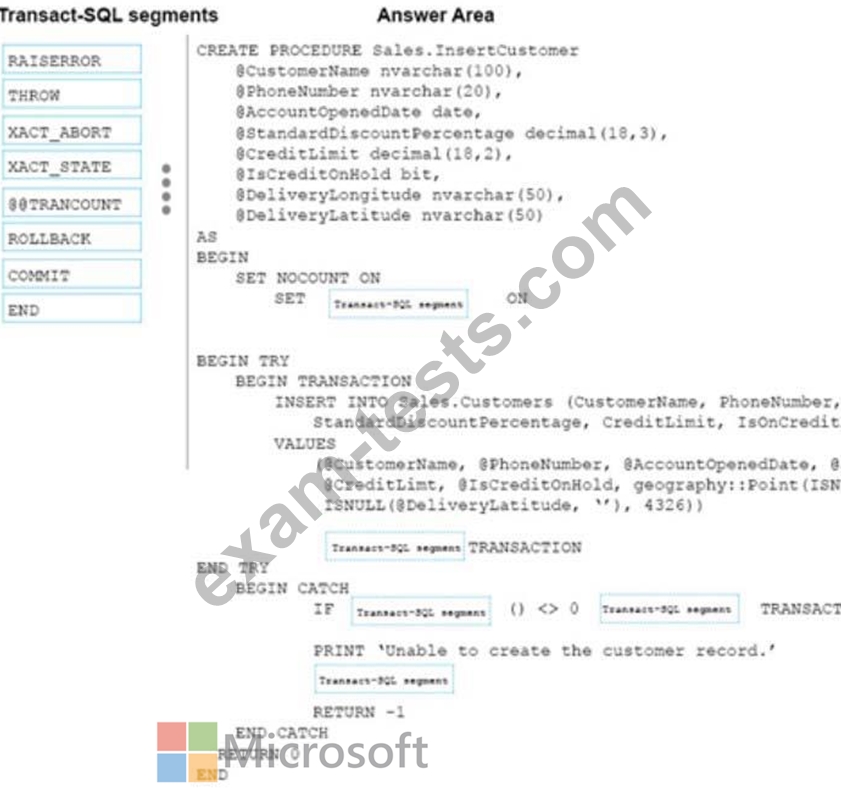
You need to create a stored procedure that inserts data into the Customers table. The stored procedure must meet the following requirements:
Data changes occur as a single unit of work.

Data modifications that are successful are committed and a value of 0 is returned.

Data modifications that are unsuccessful are rolled back. The exception severity level is set to 16 and a

value of -1 is returned.
The stored procedure uses a built-it scalar function to evaluate the current condition of data

modifications.
The entire unit of work is terminated and rolled back if a run-time error occurs during execution of the

stored procedure.
How should complete the stored procedure definition? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL segments to the correct targets. Each Transact-SQL segment may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You are developing a database to track customer orders. The database contains the following tables:
Sales.Customers, Sales.Orders, and Sales.OrderLines. The following table describes the columns in Sales.Customers.

The following table describes the columns in Sales.Orders.

The following table describes the columns in Sales.OrderLines.

You need to create a stored procedure that inserts data into the Customers table. The stored procedure must meet the following requirements:
Data changes occur as a single unit of work.

Data modifications that are successful are committed and a value of 0 is returned.

Data modifications that are unsuccessful are rolled back. The exception severity level is set to 16 and a

value of -1 is returned.
The stored procedure uses a built-it scalar function to evaluate the current condition of data

modifications.
The entire unit of work is terminated and rolled back if a run-time error occurs during execution of the

stored procedure.
How should complete the stored procedure definition? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL segments to the correct targets. Each Transact-SQL segment may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:

Question 170
DRAG DROP
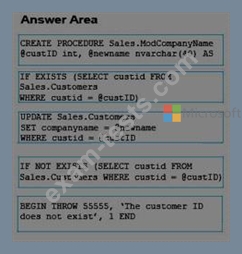
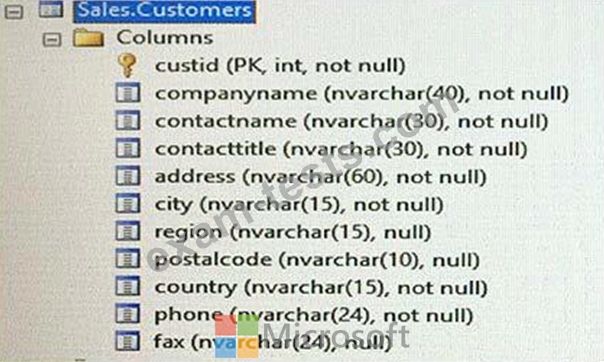
You need to create a stored procedure to update a table named Sales.Customers. The structure of the table is shown in the exhibit. (Click the exhibit button.)
The stored procedure must meet the following requirements:
-Accept two input parameters.
-Update the company name if the customer exists.
-Return a custom error message if the customer does not exist.
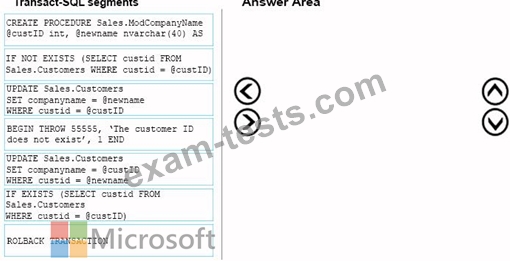
Which five Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate Transact-SQL segments from the list of Transact-SQL segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
NOTE: More than one order of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct orders you select.
You need to create a stored procedure to update a table named Sales.Customers. The structure of the table is shown in the exhibit. (Click the exhibit button.)

The stored procedure must meet the following requirements:
-Accept two input parameters.
-Update the company name if the customer exists.
-Return a custom error message if the customer does not exist.
Which five Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate Transact-SQL segments from the list of Transact-SQL segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
NOTE: More than one order of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct orders you select.