Question 126
A crucial database, 'db_prod', just disappeared from your production MySQL instance.
In reviewing the available MySQL logs (General, Audit, or Slow) and your own application-level logs, you identified this command from a customer facing application:
SELECT id FROM users WHERE login='payback!';DROP DATABASE db_prod;'
Which three methods could have been used to prevent this SQL injection attack from happening?
In reviewing the available MySQL logs (General, Audit, or Slow) and your own application-level logs, you identified this command from a customer facing application:
SELECT id FROM users WHERE login='payback!';DROP DATABASE db_prod;'
Which three methods could have been used to prevent this SQL injection attack from happening?
Question 127
While attempting to set up a new replication slave on host `192.168.0.25' with the user `replication', you encounter this error:

What should you do to resolve this error?

What should you do to resolve this error?
Question 128
A simple master-to-slave replication is currently being used. This information is extracted from the SHOW SLAVE STATUS output:
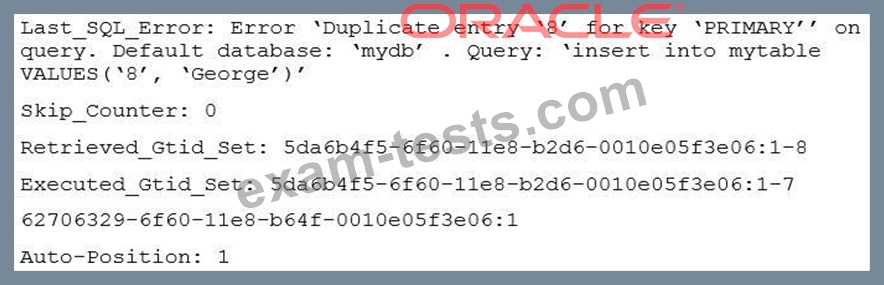
You execute a 'SHOW CREATE TABLE mytable" on the slave:

The table mytable on the slave contains:
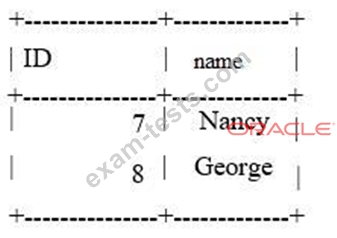
You have issued a STOP SLAVE command. You have determined that it is safe to skip the transaction in this case. One or more statements are required before you can issue a START SLAVE command to resolve the duplicate key error. Which statement should be used?

You execute a 'SHOW CREATE TABLE mytable" on the slave:

The table mytable on the slave contains:

You have issued a STOP SLAVE command. You have determined that it is safe to skip the transaction in this case. One or more statements are required before you can issue a START SLAVE command to resolve the duplicate key error. Which statement should be used?
Question 129
What are three methods to reduce MySQL server exposure to remote connections? (Choose three.)
Question 130
You are using replication and the binary log files on your master server consume a lot of disk space.
Which two steps should you perform to safely remove some of the older binary log files? (Choose two.)
Which two steps should you perform to safely remove some of the older binary log files? (Choose two.)

