Question 141
A simple master-to-slave replication is currently being used. This information is extracted from the SHOW SLAVE STATUS output:
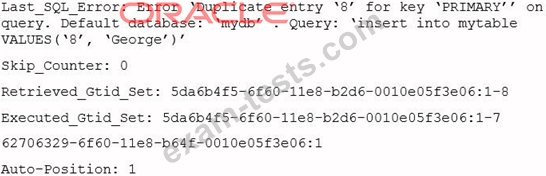
You execute a `SHOW CREATE TABLE mytable" on the slave:

The table mytable on the slave contains:
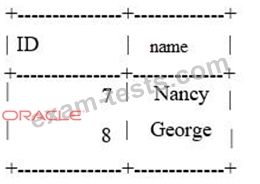
You have issued a STOP SLAVE command. You have determined that it is safe to skip the transaction in this case. One or more statements are required before you can issue a START SLAVE command to resolve the duplicate key error. Which statement should be used?

You execute a `SHOW CREATE TABLE mytable" on the slave:

The table mytable on the slave contains:

You have issued a STOP SLAVE command. You have determined that it is safe to skip the transaction in this case. One or more statements are required before you can issue a START SLAVE command to resolve the duplicate key error. Which statement should be used?
Question 142
Where does MySQL Linux RPM install the mysqld binary?
Question 143
Due to an authentication plug-in that is used on the server, passwords are required to be sent as clear text as opposed to the usual encrypted format.
Which two methods would allow the mysql client to connect to the server and send clear text passwords?
Which two methods would allow the mysql client to connect to the server and send clear text passwords?
Question 144
A MySQL replication slave is set up as follows:
* Uses all InnoDB tables
* Receives ROW-based binary logs
* Has the read-only option
The replication slave has been found in an error state.
You check the MySQL error log file and find these entries:
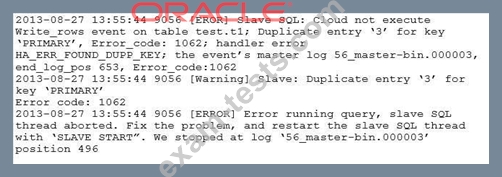
What are two possible causes for this error to occur? (Choose two.)
* Uses all InnoDB tables
* Receives ROW-based binary logs
* Has the read-only option
The replication slave has been found in an error state.
You check the MySQL error log file and find these entries:

What are two possible causes for this error to occur? (Choose two.)
Question 145
The 'applicationdb' is using InnoDB and consuming a large amount of file system space. You have a / backuppartition available on NFS where backups are stored.
You investigate and gather this information:

Three tables are stored in the InnoDB shared tablespace and the details are as follows:
* The table data_currenthas 1,000,000 rows.
* The table data_reports has 1,500,000 rows.
* The table data_archivehas 4,500,000 rows.

You attempt to free space from ibdata1by taking a mysqldump of the data_archivetable and storing it on your backup partition.
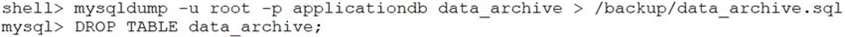
Unfortunately, this action does not free any actual disk space back to the file system and the server disk space is running out.
Which set of actions will allow you to free disk space back to the file system?
You investigate and gather this information:

Three tables are stored in the InnoDB shared tablespace and the details are as follows:
* The table data_currenthas 1,000,000 rows.
* The table data_reports has 1,500,000 rows.
* The table data_archivehas 4,500,000 rows.

You attempt to free space from ibdata1by taking a mysqldump of the data_archivetable and storing it on your backup partition.
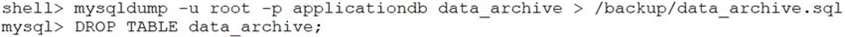
Unfortunately, this action does not free any actual disk space back to the file system and the server disk space is running out.
Which set of actions will allow you to free disk space back to the file system?

