Question 36
You inherited a busy InnoDB OLTP Instance with 100 schemas and 100 active users per schema.
* Total dataset size is 200G with an average schema size of 2G.
* The data is transient and is not backed up and can be repopulated easily.
* Performance and responsiveness of the DB is paramount.
* The query pattern for the DB instance is split 90/10 read/write.
* DB host is dedicated server with 256G RAM and 64 cores.
One of your colleagues made some recent changes to the system and users are now complaining of performance impacts.
Which four configuration file edits might your colleague have performed to cause the negative DB performance?
* Total dataset size is 200G with an average schema size of 2G.
* The data is transient and is not backed up and can be repopulated easily.
* Performance and responsiveness of the DB is paramount.
* The query pattern for the DB instance is split 90/10 read/write.
* DB host is dedicated server with 256G RAM and 64 cores.
One of your colleagues made some recent changes to the system and users are now complaining of performance impacts.
Which four configuration file edits might your colleague have performed to cause the negative DB performance?
Question 37
SQL injection is a common security threat.
Which two methods would help protect against this risk? (Choose two.)
Which two methods would help protect against this risk? (Choose two.)
Question 38
Which two capabilities are granted with the SUPER privilege? (Choose two.)
Question 39
You are investigating the performance of a query which selects data from an InnoDB table.
Consider this Performance Schema diagnostics output for the query:
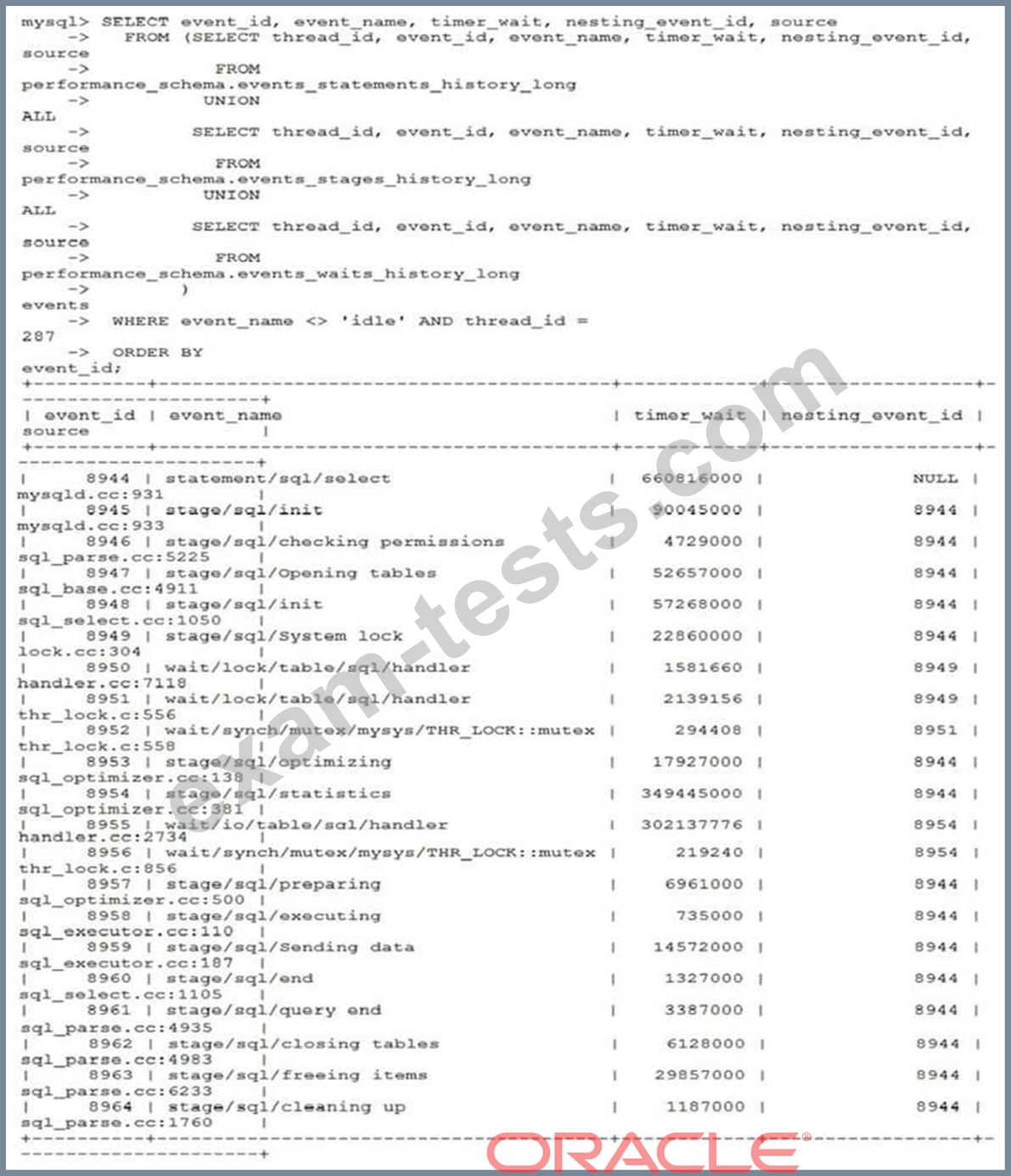
Which statement is true about the output?
Consider this Performance Schema diagnostics output for the query:

Which statement is true about the output?
Question 40
A simple master-to-slave replication is currently being used. This information is extracted from the SHOW SLAVE STATUS output:
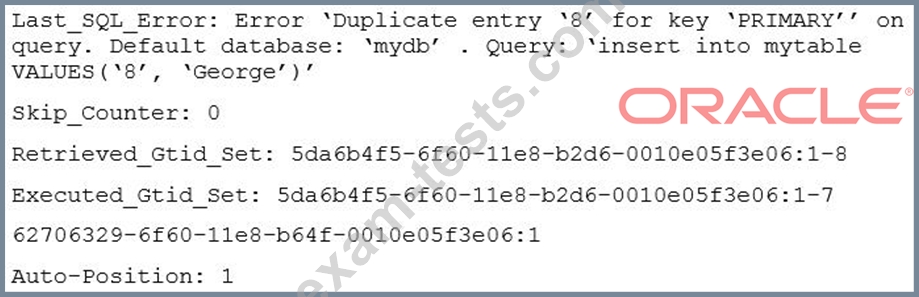
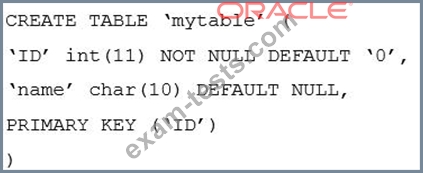
You execute a 'SHOW CREATE TABLE mytable" on the slave:
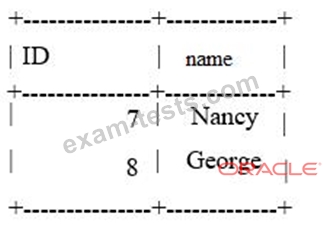
The table mytable on the slave contains:
You have issued a STOP SLAVE command. You have determined that it is safe to skip the transaction in this case. One or more statements are required before you can issue a START SLAVE command to resolve the duplicate key error. Which statement should be used?

You execute a 'SHOW CREATE TABLE mytable" on the slave:

The table mytable on the slave contains:

You have issued a STOP SLAVE command. You have determined that it is safe to skip the transaction in this case. One or more statements are required before you can issue a START SLAVE command to resolve the duplicate key error. Which statement should be used?

