Question 126
Given that data.txt and alldata.txt are accessible, and the code fragment:

What is required at line n1 to enable the code to overwrite alldata.txt with data.txt?

What is required at line n1 to enable the code to overwrite alldata.txt with data.txt?
Question 127
Given:

and the code fragment:

What is the result?

and the code fragment:

What is the result?
Question 128
Given the code fragment:

What is the result?

What is the result?
Question 129
Given the code fragment:
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader brCopy = null;
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new FileReader
("employee.txt"))) { //
line n1
br.lines().forEach(c -> System.out.println(c));
brCopy = br; //line n2
}
brCopy.ready(); //line n3;
}
Assume that the ready method of the BufferedReader, when called on a closed BufferedReader, throws an exception, and employee.txt is accessible and contains valid text.
What is the result?
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader brCopy = null;
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new FileReader
("employee.txt"))) { //
line n1
br.lines().forEach(c -> System.out.println(c));
brCopy = br; //line n2
}
brCopy.ready(); //line n3;
}
Assume that the ready method of the BufferedReader, when called on a closed BufferedReader, throws an exception, and employee.txt is accessible and contains valid text.
What is the result?
Question 130
Given the code fragment:
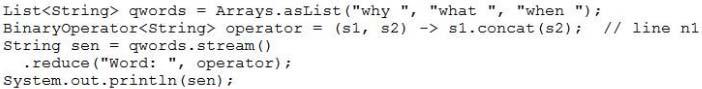
What is the result?
Word: why what when
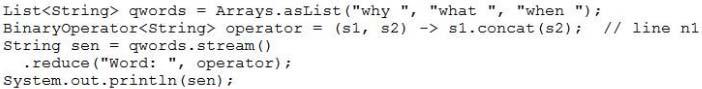
What is the result?
Word: why what when

