Question 46
Given the code fragment:
List<Integer> list1 = Arrays.asList(10, 20);
List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(15, 30);
//line n1
Which code fragment, when inserted at line n1, prints 10 20 15 30?
List<Integer> list1 = Arrays.asList(10, 20);
List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(15, 30);
//line n1
Which code fragment, when inserted at line n1, prints 10 20 15 30?
Question 47
Given:
public class Test<T> {
private T t;
public T get () {
return t;
}
public void set (T t) {
this.t = t;
}
public static void main (String args [ ] ) {
Test<String> type = new Test<>();
Test type 1 = new Test ();//line n1
type.set("Java");
type1.set(100);//line n2
System.out.print(type.get() + " " + type1.get());
}
}
What is the result?
public class Test<T> {
private T t;
public T get () {
return t;
}
public void set (T t) {
this.t = t;
}
public static void main (String args [ ] ) {
Test<String> type = new Test<>();
Test type 1 = new Test ();//line n1
type.set("Java");
type1.set(100);//line n2
System.out.print(type.get() + " " + type1.get());
}
}
What is the result?
Question 48
Given the code fragments:
4 . void doStuff() throws ArithmeticException, NumberFormatException, Exception
{
5 . if (Math.random() >-1 throw new Exception ("Try again");
6 . }
and
2 4. try {
2 5. doStuff ( ):
2 6. } catch (ArithmeticException | NumberFormatException | Exception e) {
2 7. System.out.println (e.getMessage()); }
2 8. catch (Exception e) {
2 9. System.out.println (e.getMessage()); }
3 0. }
Which modification enables the code to print Try again?
4 . void doStuff() throws ArithmeticException, NumberFormatException, Exception
{
5 . if (Math.random() >-1 throw new Exception ("Try again");
6 . }
and
2 4. try {
2 5. doStuff ( ):
2 6. } catch (ArithmeticException | NumberFormatException | Exception e) {
2 7. System.out.println (e.getMessage()); }
2 8. catch (Exception e) {
2 9. System.out.println (e.getMessage()); }
3 0. }
Which modification enables the code to print Try again?
Question 49
Given the code fragment:
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader brCopy = null;
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new FileReader
( "employee.txt"))) { //
line n1
br.lines().forEach(c -> System.out.println(c));
brCopy = br; //line n2
}
brCopy.ready(); //line n3;
}
Assume that the ready method of the BufferedReader, when called on a closed BufferedReader, throws an exception, and employee.txt is accessible and contains valid text.
What is the result?
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader brCopy = null;
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new FileReader
( "employee.txt"))) { //
line n1
br.lines().forEach(c -> System.out.println(c));
brCopy = br; //line n2
}
brCopy.ready(); //line n3;
}
Assume that the ready method of the BufferedReader, when called on a closed BufferedReader, throws an exception, and employee.txt is accessible and contains valid text.
What is the result?
Question 50
Given the code fragment:
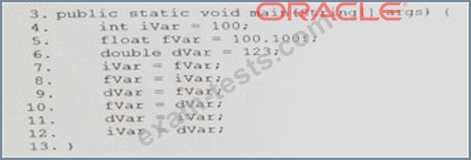
Which three lines fail to compile?

Which three lines fail to compile?

