- Home
- ISACA Certification
- CISA Exam
- ISACA.CISA.v2024-10-22.q310 Practice Test
Question 101
Identify the WAN message switching technique being used from the description presented below:
"Data is routed in its entirety from the source node to the destination node, one hope at a time. During message routing, every intermediate switch in the network stores the whole message. If the entire network's resources are engaged or the network becomes blocked, this WAN switching technology stores and delays the message until ample resources become available for effective transmission of the message. "
"Data is routed in its entirety from the source node to the destination node, one hope at a time. During message routing, every intermediate switch in the network stores the whole message. If the entire network's resources are engaged or the network becomes blocked, this WAN switching technology stores and delays the message until ample resources become available for effective transmission of the message. "
Correct Answer: A
Explanation/Reference:
For your exam you should know below information about WAN message transmission technique:
Message Switching
Message switching is a network switching technique in which data is routed in its entirety from the source node to the destination node, one hope at a time. During message routing, every intermediate switch in the network stores the whole message. If the entire network's resources are engaged or the network becomes blocked, the message-switched network stores and delays the message until ample resources become available for effective transmission of the message.
Message Switching
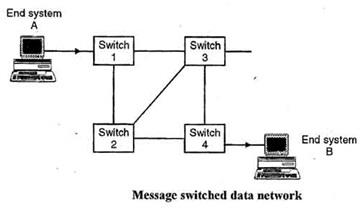
Image from: http://ecomputernotes.com/images/Message-Switched-data-Network.jpg Packet Switching
Refers to protocols in which messages are divided into packets before they are sent. Each packet is then transmitted individually and can even follow different routes to its destination. Once all the packets forming a message arrive at the destination, they are recompiled into the original message.
Packet Switching
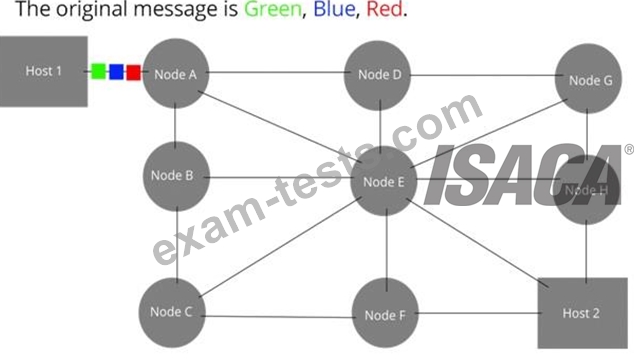
Image from: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f6/Packet_Switching.gif Circuit Switching
Circuit switching is a methodology of implementing a telecommunications network in which two network nodes establish a dedicated communications channel (circuit) through the network before the nodes may communicate.
The circuit guarantees the full bandwidth of the channel and remains connected for the duration of the session. The circuit functions as if the nodes were physically connected similar to an electrical circuit.
The defining example of a circuit-switched network is the early analog telephone network. When a call is made from one telephone to another, switches within the telephone exchanges create a continuous wire circuit between the two telephones, for as long as the call lasts.
In circuit switching, the bit delay is constant during a connection, as opposed to packet switching, where packet queues may cause varying and potentially indefinitely long packet transfer delays. No circuit can be degraded by competing users because it is protected from use by other callers until the circuit is released and a new connection is set up. Even if no actual communication is taking place, the channel remains reserved and protected from competing users.
Circuit Switching
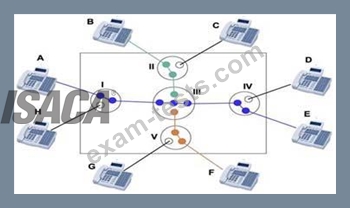
Image from: http://www.louiewong.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/Circuit_Switching.jpg See a table below comparing Circuit Switched versus Packet Switched networks:
Difference between Circuit and packet switching
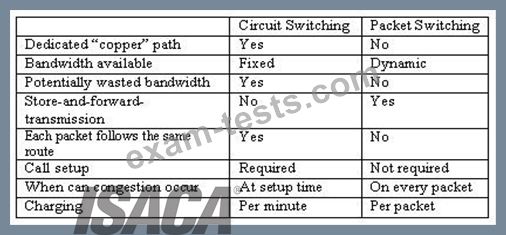
Image from:http://www.hardware-one.com/reviews/network-guide-2/images/packet-vs-circuit.gif Virtual circuit
In telecommunications and computer networks, a virtual circuit (VC), synonymous with virtual connection and virtual channel, is a connection oriented communication service that is delivered by means of packet mode communication.
After a connection or virtual circuit is established between two nodes or application processes, a bit stream or byte stream may be delivered between the nodes; a virtual circuit protocol allows higher level protocols to avoid dealing with the division of data into segments, packets, or frames.
Virtual circuit communication resembles circuit switching, since both are connection oriented, meaning that in both cases data is delivered in correct order, and signaling overhead is required during a connection establishment phase. However, circuit switching provides constant bit rate and latency, while these may vary in a virtual circuit service due to factors such as:
varying packet queue lengths in the network nodes,
varying bit rate generated by the application,
varying load from other users sharing the same network resources by means of statistical multiplexing, etc.
The following were incorrect answers:
The other options presented are not valid choices.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 Page number 265
For your exam you should know below information about WAN message transmission technique:
Message Switching
Message switching is a network switching technique in which data is routed in its entirety from the source node to the destination node, one hope at a time. During message routing, every intermediate switch in the network stores the whole message. If the entire network's resources are engaged or the network becomes blocked, the message-switched network stores and delays the message until ample resources become available for effective transmission of the message.
Message Switching

Image from: http://ecomputernotes.com/images/Message-Switched-data-Network.jpg Packet Switching
Refers to protocols in which messages are divided into packets before they are sent. Each packet is then transmitted individually and can even follow different routes to its destination. Once all the packets forming a message arrive at the destination, they are recompiled into the original message.
Packet Switching

Image from: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f6/Packet_Switching.gif Circuit Switching
Circuit switching is a methodology of implementing a telecommunications network in which two network nodes establish a dedicated communications channel (circuit) through the network before the nodes may communicate.
The circuit guarantees the full bandwidth of the channel and remains connected for the duration of the session. The circuit functions as if the nodes were physically connected similar to an electrical circuit.
The defining example of a circuit-switched network is the early analog telephone network. When a call is made from one telephone to another, switches within the telephone exchanges create a continuous wire circuit between the two telephones, for as long as the call lasts.
In circuit switching, the bit delay is constant during a connection, as opposed to packet switching, where packet queues may cause varying and potentially indefinitely long packet transfer delays. No circuit can be degraded by competing users because it is protected from use by other callers until the circuit is released and a new connection is set up. Even if no actual communication is taking place, the channel remains reserved and protected from competing users.
Circuit Switching

Image from: http://www.louiewong.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/Circuit_Switching.jpg See a table below comparing Circuit Switched versus Packet Switched networks:
Difference between Circuit and packet switching

Image from:http://www.hardware-one.com/reviews/network-guide-2/images/packet-vs-circuit.gif Virtual circuit
In telecommunications and computer networks, a virtual circuit (VC), synonymous with virtual connection and virtual channel, is a connection oriented communication service that is delivered by means of packet mode communication.
After a connection or virtual circuit is established between two nodes or application processes, a bit stream or byte stream may be delivered between the nodes; a virtual circuit protocol allows higher level protocols to avoid dealing with the division of data into segments, packets, or frames.
Virtual circuit communication resembles circuit switching, since both are connection oriented, meaning that in both cases data is delivered in correct order, and signaling overhead is required during a connection establishment phase. However, circuit switching provides constant bit rate and latency, while these may vary in a virtual circuit service due to factors such as:
varying packet queue lengths in the network nodes,
varying bit rate generated by the application,
varying load from other users sharing the same network resources by means of statistical multiplexing, etc.
The following were incorrect answers:
The other options presented are not valid choices.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 Page number 265
Question 102
Which of the following statement INCORRECTLY describes Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) technique?
Correct Answer: C
Explanation/Reference:
The keyword INCORRECTLY is used within the question. You need to find out a statement which was incorrectly describe Asynchronous Transfer Mode.ATM operates at data link layer of an OSI model For your exam you should know below information about WAN Technologies:
Point-to-point protocol
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol for communication between two computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer connected by phone line to a server. For example, your Internet server provider may provide you with a PPP connection so that the provider's server can respond to your requests, pass them on to the Internet, and forward your requested Internet responses back to you. PPP uses the Internet protocol (IP) (and is designed to handle others). It is sometimes considered a member of the TCP/IP suite of protocols. Relative to the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model, PPP provides layer 2 (data-link layer) service. Essentially, it packages your computer's TCP/IP packets and forwards them to the server where they can actually be put on the Internet.
PPP is a full-duplex protocol that can be used on various physical media, including twisted pair or fiber optic lines or satellite transmission. It uses a variation of High Speed Data Link Control (HDLC) for packet encapsulation.
PPP is usually preferred over the earlier de facto standard Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) because it can handle synchronous as well as asynchronous communication. PPP can share a line with other users and it has error detection that SLIP lacks. Where a choice is possible, PPP is preferred.
Point-to-point protocol
X.25
X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet switched wide area network (WAN) communication.
X.25 is a packet switching technology which uses carrier switch to provide connectivity for many different networks.
Subscribers are charged based on amount of bandwidth they use. Data are divided into 128 bytes and encapsulated in High Level Data Link Control (HDLC).
X.25 works at network and data link layer of an OSI model.
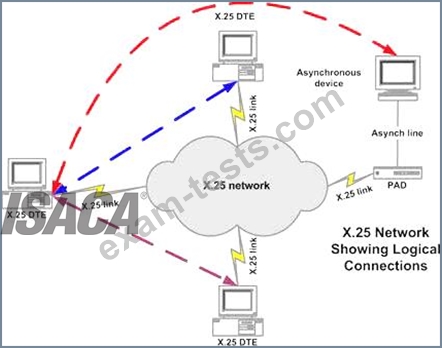
X.25
Frame Relay
Works on a packet switching
Operates at data link layer of an OSI model
Companies that pay more to ensure that a higher level of bandwidth will always be available, pay a committed information rate or CIR Two main types of equipment's are used in Frame Relay
1. Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) - Usually a customer owned device that provides a connectivity between company's own network and the frame relay's network.
2. Data Circuit Terminal Equipment (DCE) - Service provider device that does the actual data transmission and switching in the frame relay cloud.
The Frame relay cloud is the collection of DCE that provides that provides switching and data communication functionality. Frame relay is any to any service.

Frame Relay
Integrated Service Digital Network
Enables data, voice and other types of traffic to travel over a medium in a digital manner previously used only for analog voice transmission.
Same copper telephone wire is used.
Provide digital point-to-point circuit switching medium.
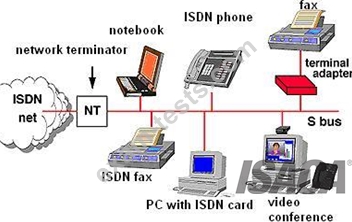
ISDN
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
Uses Cell switching method
High speed network technology used for LAN, MAN and WAN
Like a frame relay it is connection oriented technology which creates and uses fixed channel Data are segmented into fixed size cell of 53 bytes Some companies have replaces FDDI back-end with ATM
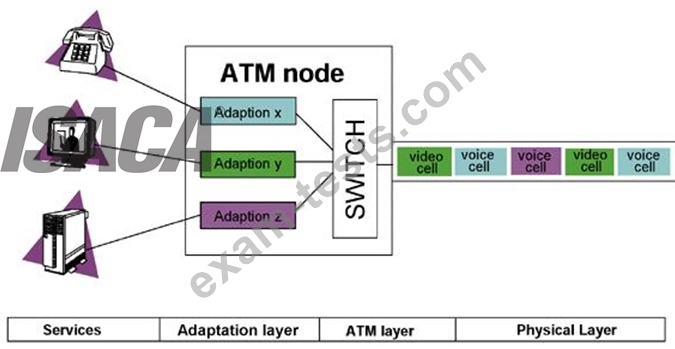
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standards-approved technology for speeding up network traffic flow and making it easier to manage. MPLS involves setting up a specific path for a given sequence of packets, identified by a label put in each packet, thus saving the time needed for a router to look up the address to the next node to forward the packet to. MPLS is called multiprotocol because it works with the Internet Protocol (IP), Asynchronous Transport Mode (ATM), and frame relay network protocols. With reference to the standard model for a network (the Open Systems Interconnection, or OSI model), MPLS allows most packets to be forwarded at the Layer 2 (switching) level rather than at the Layer 3 (routing) level. In addition to moving traffic faster overall, MPLS makes it easy to manage a network for quality of service (QoS). For these reasons, the technique is expected to be readily adopted as networks begin to carry more and different mixtures of traffic.
MPLS
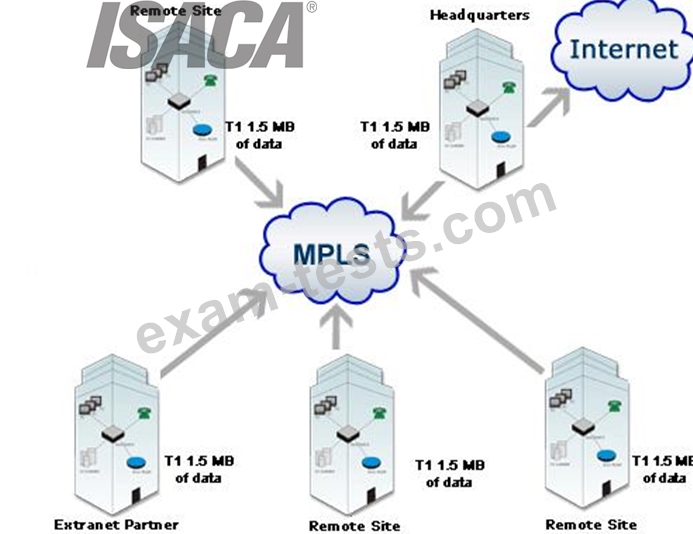
The following answers are incorrect:
The other options presented correctly describes Asynchronous Transfer Mode.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 266
The keyword INCORRECTLY is used within the question. You need to find out a statement which was incorrectly describe Asynchronous Transfer Mode.ATM operates at data link layer of an OSI model For your exam you should know below information about WAN Technologies:
Point-to-point protocol
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol for communication between two computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer connected by phone line to a server. For example, your Internet server provider may provide you with a PPP connection so that the provider's server can respond to your requests, pass them on to the Internet, and forward your requested Internet responses back to you. PPP uses the Internet protocol (IP) (and is designed to handle others). It is sometimes considered a member of the TCP/IP suite of protocols. Relative to the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model, PPP provides layer 2 (data-link layer) service. Essentially, it packages your computer's TCP/IP packets and forwards them to the server where they can actually be put on the Internet.
PPP is a full-duplex protocol that can be used on various physical media, including twisted pair or fiber optic lines or satellite transmission. It uses a variation of High Speed Data Link Control (HDLC) for packet encapsulation.
PPP is usually preferred over the earlier de facto standard Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) because it can handle synchronous as well as asynchronous communication. PPP can share a line with other users and it has error detection that SLIP lacks. Where a choice is possible, PPP is preferred.
Point-to-point protocol
X.25
X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet switched wide area network (WAN) communication.
X.25 is a packet switching technology which uses carrier switch to provide connectivity for many different networks.
Subscribers are charged based on amount of bandwidth they use. Data are divided into 128 bytes and encapsulated in High Level Data Link Control (HDLC).
X.25 works at network and data link layer of an OSI model.

X.25
Frame Relay
Works on a packet switching
Operates at data link layer of an OSI model
Companies that pay more to ensure that a higher level of bandwidth will always be available, pay a committed information rate or CIR Two main types of equipment's are used in Frame Relay
1. Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) - Usually a customer owned device that provides a connectivity between company's own network and the frame relay's network.
2. Data Circuit Terminal Equipment (DCE) - Service provider device that does the actual data transmission and switching in the frame relay cloud.
The Frame relay cloud is the collection of DCE that provides that provides switching and data communication functionality. Frame relay is any to any service.

Frame Relay
Integrated Service Digital Network
Enables data, voice and other types of traffic to travel over a medium in a digital manner previously used only for analog voice transmission.
Same copper telephone wire is used.
Provide digital point-to-point circuit switching medium.

ISDN
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
Uses Cell switching method
High speed network technology used for LAN, MAN and WAN
Like a frame relay it is connection oriented technology which creates and uses fixed channel Data are segmented into fixed size cell of 53 bytes Some companies have replaces FDDI back-end with ATM

Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standards-approved technology for speeding up network traffic flow and making it easier to manage. MPLS involves setting up a specific path for a given sequence of packets, identified by a label put in each packet, thus saving the time needed for a router to look up the address to the next node to forward the packet to. MPLS is called multiprotocol because it works with the Internet Protocol (IP), Asynchronous Transport Mode (ATM), and frame relay network protocols. With reference to the standard model for a network (the Open Systems Interconnection, or OSI model), MPLS allows most packets to be forwarded at the Layer 2 (switching) level rather than at the Layer 3 (routing) level. In addition to moving traffic faster overall, MPLS makes it easy to manage a network for quality of service (QoS). For these reasons, the technique is expected to be readily adopted as networks begin to carry more and different mixtures of traffic.
MPLS

The following answers are incorrect:
The other options presented correctly describes Asynchronous Transfer Mode.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 266
Question 103
Reverse proxy technology for web servers should be deployed if:
Correct Answer: A
Explanation/Reference:
Explanation:
Reverse proxies are primarily designed to hide physical and logical internal structures from outside access.
Complete URLs or URIs can be partially or completely redirected without disclosing which internal or DMZ server is providing the requested data. This technology might be used if a trade-off between security, performance and costs has to be achieved. Proxy servers cache some data but normally cannot cache all pages to be published because this depends on the kind of information the web servers provide. The ability to accelerate access depends on the speed of the back-end servers, i.e., those that are cached. Thus, without making further assumptions, a gain in speed cannot be assured, but visualization and hiding of internal structures can. If speed is an issue, a scale-out approach (avoiding adding additional delays by passing firewalls, involving more servers, etc.) would be a better solution. Due to the limited caching option, reverse proxies are not suitable for enhancing fault tolerance. User requests that are handled by reverse proxy servers are using exactly the same bandwidth as direct requests to the hosts providing the data.
Explanation:
Reverse proxies are primarily designed to hide physical and logical internal structures from outside access.
Complete URLs or URIs can be partially or completely redirected without disclosing which internal or DMZ server is providing the requested data. This technology might be used if a trade-off between security, performance and costs has to be achieved. Proxy servers cache some data but normally cannot cache all pages to be published because this depends on the kind of information the web servers provide. The ability to accelerate access depends on the speed of the back-end servers, i.e., those that are cached. Thus, without making further assumptions, a gain in speed cannot be assured, but visualization and hiding of internal structures can. If speed is an issue, a scale-out approach (avoiding adding additional delays by passing firewalls, involving more servers, etc.) would be a better solution. Due to the limited caching option, reverse proxies are not suitable for enhancing fault tolerance. User requests that are handled by reverse proxy servers are using exactly the same bandwidth as direct requests to the hosts providing the data.
Question 104
Which of the following is MOST effective for controlling visitor access to a data center?
Correct Answer: B
Question 105
When developing a business continuity plan (BCP), which of the following should be performed FIRST?
Correct Answer: C
Section: Protection of Information Assets
Explanation/Reference:
Explanation/Reference:
- Other Version
- 4563ISACA.CISA.v2025-05-24.q773
- 4136ISACA.CISA.v2023-10-02.q715
- 3738ISACA.CISA.v2023-03-29.q119
- 2387ISACA.CISA.v2023-02-09.q181
- 1498ISACA.CISA.v2023-02-06.q107
- 3051ISACA.CISA.v2022-08-28.q129
- 4218ISACA.CISA.v2022-02-25.q148
- 126ISACA.Actualtestpdf.CISA.v2021-11-13.by.sarah.721q.pdf
- 5623ISACA.CISA.v2021-11-11.q194
- 8818ISACA.CISA.v2021-10-08.q198
- 9794ISACA.CISA.v2021-09-28.q199
- 12254ISACA.CISA.v2021-09-11.q201
- Latest Upload
- 105OCEG.GRCP.v2025-09-11.q211
- 104HP.HPE0-V27.v2025-09-11.q78
- 118Oracle.1Z0-1057-23.v2025-09-10.q47
- 150Google.Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer.v2025-09-09.q179
- 131SAP.C-S4EWM-2023.v2025-09-08.q83
- 165TheSecOpsGroup.CNSP.v2025-09-08.q20
- 223CFAInstitute.ESG-Investing.v2025-09-08.q173
- 158PECB.ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Implementer.v2025-09-06.q132
- 150Salesforce.Data-Architect.v2025-09-05.q216
- 144Adobe.AD0-E605.v2025-09-05.q50
[×]
Download PDF File
Enter your email address to download ISACA.CISA.v2024-10-22.q310 Practice Test

