- Home
- ISACA Certification
- CISA Exam
- ISACA.CISA.v2025-05-24.q773 Practice Test
Question 81
The PRIMARY benefit of implementing a security program as part of a security governance framework is
the:
the:
Correct Answer: B
Section: Protection of Information Assets
Explanation:
The major benefit of implementing a security program is management's assessment of risk and its
mitigation to an appropriate level of risk, and the monitoring of the remaining residual risks.
Recommendations, visions and objectives of the auditor and the chief information security officer (CISO)
are usually included within a security program, but they would not be the major benefit.
The cost of IT security may or may not be reduced.
Explanation:
The major benefit of implementing a security program is management's assessment of risk and its
mitigation to an appropriate level of risk, and the monitoring of the remaining residual risks.
Recommendations, visions and objectives of the auditor and the chief information security officer (CISO)
are usually included within a security program, but they would not be the major benefit.
The cost of IT security may or may not be reduced.
Question 82
The FIRST step in auditing a data communication system is to determine:
Correct Answer: D
Explanation
The first step in auditing a data communication system is to determine the business use and types of messages to be transmitted. This is because the auditor needs to understand the purpose, scope, and objectives of the data communication system, as well as the nature, volume, and sensitivity of the data being transmitted. This will help the auditor to identify the risks, controls, and audit criteria for the data communication system. Traffic volumes and response-time criteria, physical security for network equipment, and the level of redundancy in the various communication paths are important aspects of a data communication system, but they are not the first step in auditing it. They depend on the business use and types of messages to be transmitted, and they may vary according to different scenarios and requirements. References: CISA Review Manual (Digital Version), [ISACA Auditing Standards]
The first step in auditing a data communication system is to determine the business use and types of messages to be transmitted. This is because the auditor needs to understand the purpose, scope, and objectives of the data communication system, as well as the nature, volume, and sensitivity of the data being transmitted. This will help the auditor to identify the risks, controls, and audit criteria for the data communication system. Traffic volumes and response-time criteria, physical security for network equipment, and the level of redundancy in the various communication paths are important aspects of a data communication system, but they are not the first step in auditing it. They depend on the business use and types of messages to be transmitted, and they may vary according to different scenarios and requirements. References: CISA Review Manual (Digital Version), [ISACA Auditing Standards]
Question 83
When auditing an organization's software acquisition process the BEST way for an IS auditor to understand the software benefits to the organization would be to review the
Correct Answer: B
The best way for an IS auditor to understand the software benefits to the organization would be to review the business case, which is a document that provides the justification and rationale for acquiring a software solution based on its expected costs, benefits, risks, and alignment with the organization's goals and strategies.
The business case helps to evaluate the feasibility and viability of the software acquisition and to support the decision-making process. A feasibility study is a document that analyzes the technical, operational, economic, legal, and social aspects of a software solution to determine its feasibility and suitability for the organization's needs, but it does not necessarily provide a clear indication of the software benefits to the organization. A request for proposal (RFP) is a document that solicits proposals from potential vendors or suppliers for a software solution based on the organization's requirements and specifications, but it does not necessarily provide a clear indication of the software benefits to the organization. The alignment with IT strategy is a factor that influences the software acquisition process and ensures that the software solution supports and enables the organization's IT strategy, but it is not a document that can be reviewed by an IS auditor to understand the software benefits to the organization. References: CISA Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 3: Information Systems Acquisition, Development & Implementation, Section 3.1: Business Case Development
The business case helps to evaluate the feasibility and viability of the software acquisition and to support the decision-making process. A feasibility study is a document that analyzes the technical, operational, economic, legal, and social aspects of a software solution to determine its feasibility and suitability for the organization's needs, but it does not necessarily provide a clear indication of the software benefits to the organization. A request for proposal (RFP) is a document that solicits proposals from potential vendors or suppliers for a software solution based on the organization's requirements and specifications, but it does not necessarily provide a clear indication of the software benefits to the organization. The alignment with IT strategy is a factor that influences the software acquisition process and ensures that the software solution supports and enables the organization's IT strategy, but it is not a document that can be reviewed by an IS auditor to understand the software benefits to the organization. References: CISA Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 3: Information Systems Acquisition, Development & Implementation, Section 3.1: Business Case Development
Question 84
Which of the following is the INCORRECT Layer to Protocol mapping used in the DOD TCP/IP model?
Correct Answer: B
Explanation/Reference:
The keyword INCORRECT is used within the question. You need to find out the incorrect Layer to Protocol mapping.
The ICMP protocol works at Internet layer of the DoD TCP/IP model, not at the Transport Layer.
For your exam you should know below information about the TCP/IP models:
Network Models
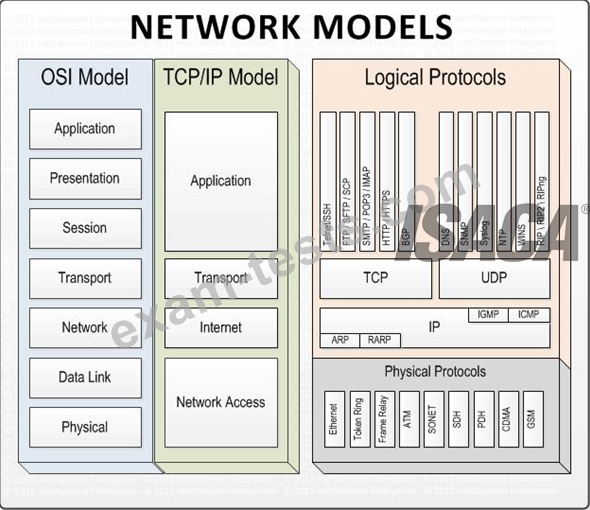
Layer 4. Application Layer
Application layer is the top most layer of four layer TCP/IP model. Application layer is present on the top of the Transport layer. Application layer defines TCP/IP application protocols and how host programs interface with Transport layer services to use the network.
Application layer includes all the higher-level protocols like DNS (Domain Naming System), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), Telnet, SSH, FTP (File Transfer Protocol), TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) , DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), X Windows, RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) etc.
Layer 3. Transport Layer
Transport Layer is the third layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. The position of the Transport layer is between Application layer and Internet layer. The purpose of Transport layer is to permit devices on the source and destination hosts to carry on a conversation. Transport layer defines the level of service and status of the connection used when transporting data.
The main protocols included at Transport layer are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
Layer 2. Internet Layer
Internet Layer is the second layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. The position of Internet layer is between Network Access Layer and Transport layer. Internet layer pack data into data packets known as IP datagram's, which contain source and destination address (logical address or IP address) information that is used to forward the datagram's between hosts and across networks. The Internet layer is also responsible for routing of IP datagram's.
Packet switching network depends upon a connectionless internetwork layer. This layer is known as Internet layer. Its job is to allow hosts to insert packets into any network and have them to deliver independently to the destination. At the destination side data packets may appear in a different order than they were sent. It is the job of the higher layers to rearrange them in order to deliver them to proper network applications operating at the Application layer.
The main protocols included at Internet layer are IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) and IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol).
Layer 1. Network Access Layer
Network Access Layer is the first layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. Network Access Layer defines details of how data is physically sent through the network, including how bits are electrically or optically signaled by hardware devices that interface directly with a network medium, such as coaxial cable, optical fiber, or twisted pair copper wire.
The protocols included in Network Access Layer are Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, X.25, Frame Relay etc.
The most popular LAN architecture among those listed above is Ethernet. Ethernet uses an Access Method called CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) to access the media, when Ethernet operates in a shared media. An Access Method determines how a host will place data on the medium.
IN CSMA/CD Access Method, every host has equal access to the medium and can place data on the wire when the wire is free from network traffic. When a host wants to place data on the wire, it will check the wire to find whether another host is already using the medium. If there is traffic already in the medium, the host will wait and if there is no traffic, it will place the data in the medium. But, if two systems place data on the medium at the same instance, they will collide with each other, destroying the data. If the data is destroyed during transmission, the data will need to be retransmitted. After collision, each host will wait for a small interval of time and again the data will be retransmitted.
Protocol Data Unit (PDU) :
Protocol Data Unit - PDU
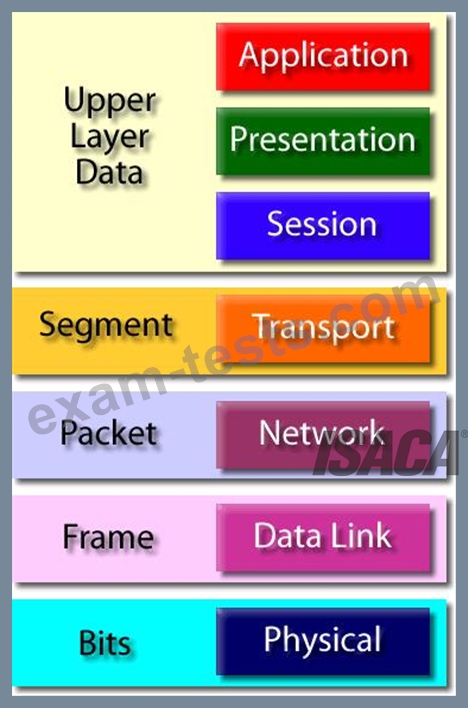
The following answers are incorrect:
The other options correctly describes the Layer to Protocol mapping of the DoD TCP/IP model protocols.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 272
The keyword INCORRECT is used within the question. You need to find out the incorrect Layer to Protocol mapping.
The ICMP protocol works at Internet layer of the DoD TCP/IP model, not at the Transport Layer.
For your exam you should know below information about the TCP/IP models:
Network Models

Layer 4. Application Layer
Application layer is the top most layer of four layer TCP/IP model. Application layer is present on the top of the Transport layer. Application layer defines TCP/IP application protocols and how host programs interface with Transport layer services to use the network.
Application layer includes all the higher-level protocols like DNS (Domain Naming System), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), Telnet, SSH, FTP (File Transfer Protocol), TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) , DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), X Windows, RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) etc.
Layer 3. Transport Layer
Transport Layer is the third layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. The position of the Transport layer is between Application layer and Internet layer. The purpose of Transport layer is to permit devices on the source and destination hosts to carry on a conversation. Transport layer defines the level of service and status of the connection used when transporting data.
The main protocols included at Transport layer are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
Layer 2. Internet Layer
Internet Layer is the second layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. The position of Internet layer is between Network Access Layer and Transport layer. Internet layer pack data into data packets known as IP datagram's, which contain source and destination address (logical address or IP address) information that is used to forward the datagram's between hosts and across networks. The Internet layer is also responsible for routing of IP datagram's.
Packet switching network depends upon a connectionless internetwork layer. This layer is known as Internet layer. Its job is to allow hosts to insert packets into any network and have them to deliver independently to the destination. At the destination side data packets may appear in a different order than they were sent. It is the job of the higher layers to rearrange them in order to deliver them to proper network applications operating at the Application layer.
The main protocols included at Internet layer are IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) and IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol).
Layer 1. Network Access Layer
Network Access Layer is the first layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. Network Access Layer defines details of how data is physically sent through the network, including how bits are electrically or optically signaled by hardware devices that interface directly with a network medium, such as coaxial cable, optical fiber, or twisted pair copper wire.
The protocols included in Network Access Layer are Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, X.25, Frame Relay etc.
The most popular LAN architecture among those listed above is Ethernet. Ethernet uses an Access Method called CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) to access the media, when Ethernet operates in a shared media. An Access Method determines how a host will place data on the medium.
IN CSMA/CD Access Method, every host has equal access to the medium and can place data on the wire when the wire is free from network traffic. When a host wants to place data on the wire, it will check the wire to find whether another host is already using the medium. If there is traffic already in the medium, the host will wait and if there is no traffic, it will place the data in the medium. But, if two systems place data on the medium at the same instance, they will collide with each other, destroying the data. If the data is destroyed during transmission, the data will need to be retransmitted. After collision, each host will wait for a small interval of time and again the data will be retransmitted.
Protocol Data Unit (PDU) :
Protocol Data Unit - PDU

The following answers are incorrect:
The other options correctly describes the Layer to Protocol mapping of the DoD TCP/IP model protocols.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 272
Question 85
Which of the following should be included in a feasibility study for a project to implement an EDI process?
Correct Answer: C
Explanation/Reference:
Explanation:
Encryption algorithms, third-party agreements and internal control procedures are too detailed for this phase. They would only be outlined and any cost or performance implications shown. The communications protocols must be included, as there may be significant cost implications if new hardware and software are involved, and risk implications if the technology is new to the organization.
Explanation:
Encryption algorithms, third-party agreements and internal control procedures are too detailed for this phase. They would only be outlined and any cost or performance implications shown. The communications protocols must be included, as there may be significant cost implications if new hardware and software are involved, and risk implications if the technology is new to the organization.
- Other Version
- 1623ISACA.CISA.v2024-10-22.q310
- 4136ISACA.CISA.v2023-10-02.q715
- 3740ISACA.CISA.v2023-03-29.q119
- 2388ISACA.CISA.v2023-02-09.q181
- 1498ISACA.CISA.v2023-02-06.q107
- 3051ISACA.CISA.v2022-08-28.q129
- 4218ISACA.CISA.v2022-02-25.q148
- 126ISACA.Actualtestpdf.CISA.v2021-11-13.by.sarah.721q.pdf
- 5623ISACA.CISA.v2021-11-11.q194
- 8826ISACA.CISA.v2021-10-08.q198
- 9799ISACA.CISA.v2021-09-28.q199
- 12255ISACA.CISA.v2021-09-11.q201
- Latest Upload
- 105OCEG.GRCP.v2025-09-11.q211
- 104HP.HPE0-V27.v2025-09-11.q78
- 118Oracle.1Z0-1057-23.v2025-09-10.q47
- 151Google.Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer.v2025-09-09.q179
- 131SAP.C-S4EWM-2023.v2025-09-08.q83
- 165TheSecOpsGroup.CNSP.v2025-09-08.q20
- 223CFAInstitute.ESG-Investing.v2025-09-08.q173
- 173PECB.ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Implementer.v2025-09-06.q132
- 151Salesforce.Data-Architect.v2025-09-05.q216
- 146Adobe.AD0-E605.v2025-09-05.q50
[×]
Download PDF File
Enter your email address to download ISACA.CISA.v2025-05-24.q773 Practice Test

