Question 1
SIMULATION
Secrets stored in the etcd is not secure at rest, you can use the etcdctl command utility to find the secret value for e.g:- ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl get /registry/secrets/default/cks-secret --cacert="ca.crt" --cert="server.crt" --key="server.key" Output
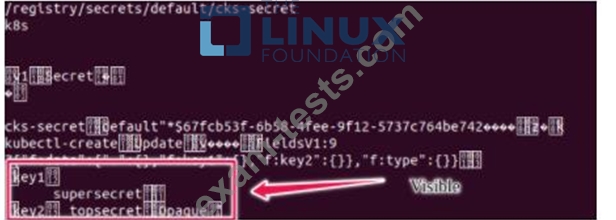
Using the Encryption Configuration, Create the manifest, which secures the resource secrets using the provider AES-CBC and identity, to encrypt the secret-data at rest and ensure all secrets are encrypted with the new configuration.
Secrets stored in the etcd is not secure at rest, you can use the etcdctl command utility to find the secret value for e.g:- ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl get /registry/secrets/default/cks-secret --cacert="ca.crt" --cert="server.crt" --key="server.key" Output

Using the Encryption Configuration, Create the manifest, which secures the resource secrets using the provider AES-CBC and identity, to encrypt the secret-data at rest and ensure all secrets are encrypted with the new configuration.
Question 2
SIMULATION
Using the runtime detection tool Falco, Analyse the container behavior for at least 20 seconds, using filters that detect newly spawning and executing processes in a single container of Nginx.
store the incident file art /opt/falco-incident.txt, containing the detected incidents. one per line, in the format
[timestamp],[uid],[processName]
Using the runtime detection tool Falco, Analyse the container behavior for at least 20 seconds, using filters that detect newly spawning and executing processes in a single container of Nginx.
store the incident file art /opt/falco-incident.txt, containing the detected incidents. one per line, in the format
[timestamp],[uid],[processName]
Question 3
SIMULATION
Service is running on port 389 inside the system, find the process-id of the process, and stores the names of all the open-files inside the /candidate/KH77539/files.txt, and also delete the binary.
Service is running on port 389 inside the system, find the process-id of the process, and stores the names of all the open-files inside the /candidate/KH77539/files.txt, and also delete the binary.
Question 4
SIMULATION
Create a RuntimeClass named untrusted using the prepared runtime handler named runsc.
Create a Pods of image alpine:3.13.2 in the Namespace default to run on the gVisor runtime class.
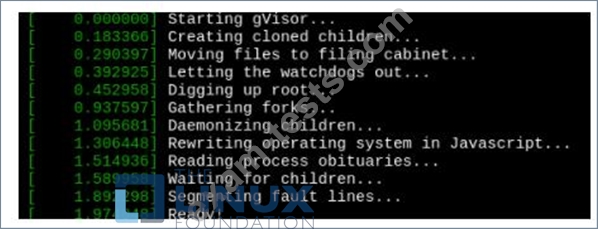
Verify: Exec the pods and run the dmesg, you will see output like this:-
Create a RuntimeClass named untrusted using the prepared runtime handler named runsc.
Create a Pods of image alpine:3.13.2 in the Namespace default to run on the gVisor runtime class.
Verify: Exec the pods and run the dmesg, you will see output like this:-

Question 5
SIMULATION
Enable audit logs in the cluster, To Do so, enable the log backend, and ensure that
1. logs are stored at /var/log/kubernetes/kubernetes-logs.txt.
2. Log files are retained for 5 days.
3. at maximum, a number of 10 old audit logs files are retained.
Edit and extend the basic policy to log:
1. Cronjobs changes at RequestResponse
2. Log the request body of deployments changes in the namespace kube-system.
3. Log all other resources in core and extensions at the Request level.
4. Don't log watch requests by the "system:kube-proxy" on endpoints or
Enable audit logs in the cluster, To Do so, enable the log backend, and ensure that
1. logs are stored at /var/log/kubernetes/kubernetes-logs.txt.
2. Log files are retained for 5 days.
3. at maximum, a number of 10 old audit logs files are retained.
Edit and extend the basic policy to log:
1. Cronjobs changes at RequestResponse
2. Log the request body of deployments changes in the namespace kube-system.
3. Log all other resources in core and extensions at the Request level.
4. Don't log watch requests by the "system:kube-proxy" on endpoints or

