Question 16
You are the Test Manager on a new project. The schedule is aggressive and will require the team to work at peak efficiency. The requirements are not well defined yet, but it is clear that the project will be using new technologies. To help the developers meet the development schedule, an offshore group will be added to the development team.
At this time there is not enough budget to add more testing resources. The project stakeholders are very concerned about the quality of delivered product and will be watching the project closely, particularly during the testing cycles. The exit criteria from the system test level require no open high priority/severity defects, 100% pass rate for all test cases covering risks that are classified as
"high" or "very high", 90% pass rate for all "medium" risks and 50% pass rate for all "low" and "very low" risks.
Given this information, which lifecycle model should you recommend?[3]
At this time there is not enough budget to add more testing resources. The project stakeholders are very concerned about the quality of delivered product and will be watching the project closely, particularly during the testing cycles. The exit criteria from the system test level require no open high priority/severity defects, 100% pass rate for all test cases covering risks that are classified as
"high" or "very high", 90% pass rate for all "medium" risks and 50% pass rate for all "low" and "very low" risks.
Given this information, which lifecycle model should you recommend?[3]
Question 17
You have directed one of your testers to construct a "smoke test" to execute against new builds prior to starting formal testing. This is an example of which software development lifecycle activity?
[1]
[1]
Question 18
Which statement about defect management in hybrid software development is TRUE?
Question 19
In general, why is it NOT a good idea to estimate the testing effort based only on a percentage of development effort? Identify THREE valid reasons. 1 credit
Question 20
You have recently implemented a new defect management process which now includes a defect triage committee whose job is to review all new defects. The process is shown in the following diagram:
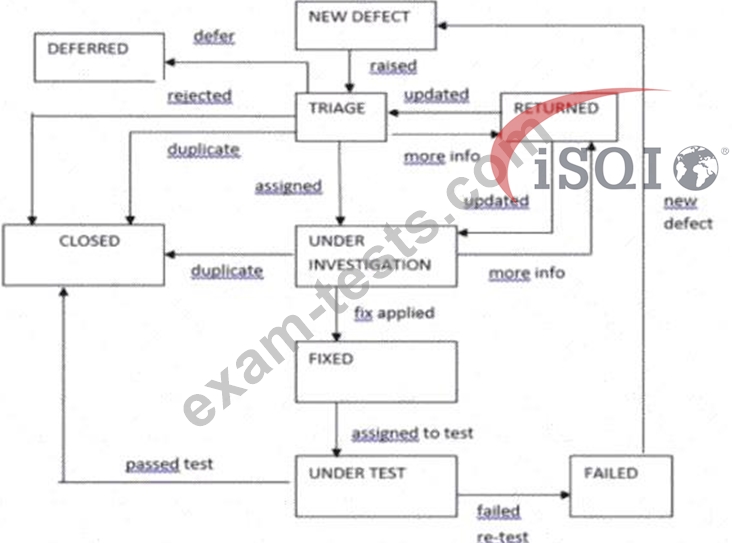
b. The total number of defects rejected as not a problem following investigation by the product author c. The number of defects returned to the defect author, expressed as a percentage of all defects raised d. The total number of defects that failed re-test more than once e. The total number of defects closed by the defect triage committee SELECT ONE OPTION

b. The total number of defects rejected as not a problem following investigation by the product author c. The number of defects returned to the defect author, expressed as a percentage of all defects raised d. The total number of defects that failed re-test more than once e. The total number of defects closed by the defect triage committee SELECT ONE OPTION

