Question 51
Refer to the exhibit.
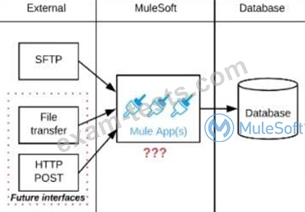
A business process involves the receipt of a file from an external vendor over SFTP. The file needs to be parsed and its content processed, validated, and ultimately persisted to a database. The delivery mechanism is expected to change in the future as more vendors send similar files using other mechanisms such as file transfer or HTTP POST.
What is the most effective way to design for these requirements in order to minimize the impact of future change?

A business process involves the receipt of a file from an external vendor over SFTP. The file needs to be parsed and its content processed, validated, and ultimately persisted to a database. The delivery mechanism is expected to change in the future as more vendors send similar files using other mechanisms such as file transfer or HTTP POST.
What is the most effective way to design for these requirements in order to minimize the impact of future change?
Question 52
Refer to the exhibit.
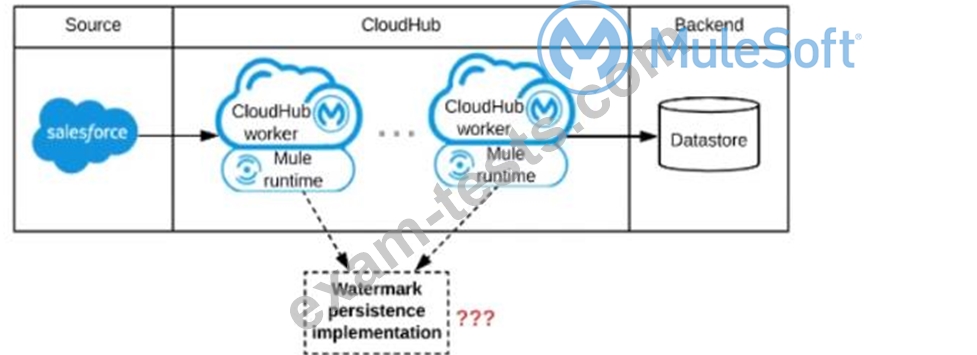
A Mule application is being designed to be deployed to several CIoudHub workers. The Mule application's integration logic is to replicate changed Accounts from Satesforce to a backend system every 5 minutes.
A watermark will be used to only retrieve those Satesforce Accounts that have been modified since the last time the integration logic ran.
What is the most appropriate way to implement persistence for the watermark in order to support the required data replication integration logic?

A Mule application is being designed to be deployed to several CIoudHub workers. The Mule application's integration logic is to replicate changed Accounts from Satesforce to a backend system every 5 minutes.
A watermark will be used to only retrieve those Satesforce Accounts that have been modified since the last time the integration logic ran.
What is the most appropriate way to implement persistence for the watermark in order to support the required data replication integration logic?
Question 53
Refer to the exhibit.
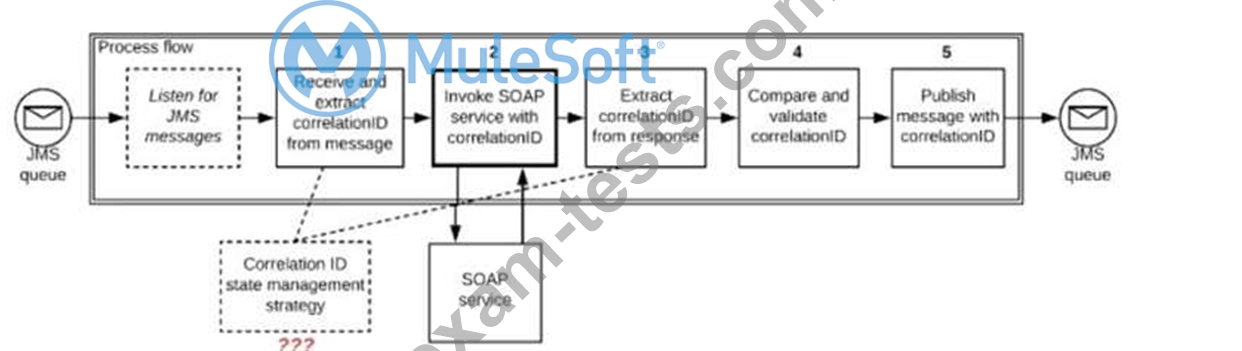
A Mule application is deployed to a multi-node Mule runtime cluster. The Mule application uses the competing consumer pattern among its cluster replicas to receive JMS messages from a JMS queue. To process each received JMS message, the following steps are performed in a flow:
Step l: The JMS Correlation ID header is read from the received JMS message.
Step 2: The Mule application invokes an idempotent SOAP webservice over HTTPS, passing the JMS Correlation ID as one parameter in the SOAP request.
Step 3: The response from the SOAP webservice also returns the same JMS Correlation ID.
Step 4: The JMS Correlation ID received from the SOAP webservice is validated to be identical to the JMS Correlation ID received in Step 1.
Step 5: The Mule application creates a response JMS message, setting the JMS Correlation ID message header to the validated JMS Correlation ID and publishes that message to a response JMS queue.
Where should the Mule application store the JMS Correlation ID values received in Step 1 and Step 3 so that the validation in Step 4 can be performed, while also making the overall Mule application highly available, fault-tolerant, performant, and maintainable?

A Mule application is deployed to a multi-node Mule runtime cluster. The Mule application uses the competing consumer pattern among its cluster replicas to receive JMS messages from a JMS queue. To process each received JMS message, the following steps are performed in a flow:
Step l: The JMS Correlation ID header is read from the received JMS message.
Step 2: The Mule application invokes an idempotent SOAP webservice over HTTPS, passing the JMS Correlation ID as one parameter in the SOAP request.
Step 3: The response from the SOAP webservice also returns the same JMS Correlation ID.
Step 4: The JMS Correlation ID received from the SOAP webservice is validated to be identical to the JMS Correlation ID received in Step 1.
Step 5: The Mule application creates a response JMS message, setting the JMS Correlation ID message header to the validated JMS Correlation ID and publishes that message to a response JMS queue.
Where should the Mule application store the JMS Correlation ID values received in Step 1 and Step 3 so that the validation in Step 4 can be performed, while also making the overall Mule application highly available, fault-tolerant, performant, and maintainable?
Question 54
Refer to the exhibit.
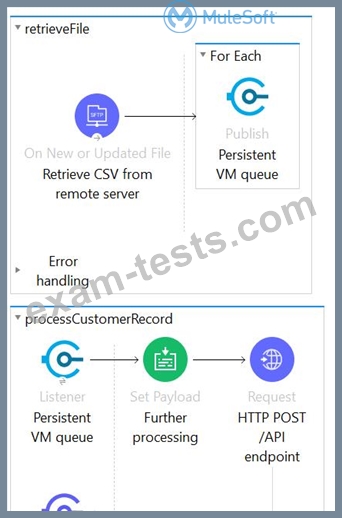
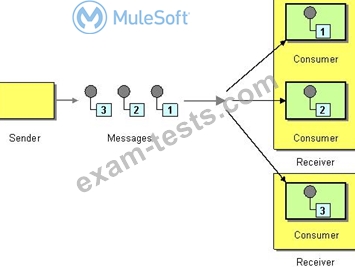
This Mule application is deployed to multiple Cloudhub workers with persistent queue enabled. The retrievefile flow event source reads a CSV file from a remote SFTP server and then publishes each record in the CSV file to a VM queue. The processCustomerRecords flow's VM Listner receives messages from the same VM queue and then processes each message separately.
How are messages routed to the cloudhub workers as messages are received by the VM Listener?

This Mule application is deployed to multiple Cloudhub workers with persistent queue enabled. The retrievefile flow event source reads a CSV file from a remote SFTP server and then publishes each record in the CSV file to a VM queue. The processCustomerRecords flow's VM Listner receives messages from the same VM queue and then processes each message separately.
How are messages routed to the cloudhub workers as messages are received by the VM Listener?
Question 55
A set of integration Mule applications, some of which expose APIs, are being created to enable a new business process. Various stakeholders may be impacted by this. These stakeholders are a combination of semi- technical users (who understand basic integration terminology and concepts such as JSON and XML) and technically skilled potential consumers of the Mule applications and APIs.
What is an effective way for the project team responsible for the Mule applications and APIs being built to communicate with these stakeholders using Anypoint Platform and its supplied toolset?
What is an effective way for the project team responsible for the Mule applications and APIs being built to communicate with these stakeholders using Anypoint Platform and its supplied toolset?