- Home
- ISACA Certification
- CISA Exam
- ISACA.CISA.v2024-10-22.q310 Practice Test
Question 186
Which of the following should an IS auditor expect to see in a network vulnerability assessment?
Correct Answer: A
A network vulnerability assessment is a process of identifying and evaluating the weaknesses and exposures in a network that could be exploited by attackers to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the network or its resources. A network vulnerability assessment typically involves scanning the network devices, such as routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and workstations, using automated tools that compare the device configurations, software versions, and patch levels against a database of known vulnerabilities. A network vulnerability assessment can also include manual testing and verification of the network architecture, design, policies, and procedures. One of the main objectives of a network vulnerability assessment is to detect and report any misconfiguration and missing updates in the network devices that could pose a security risk1.
Misconfiguration refers to any deviation from the recommended or best practice settings for the network devices, such as weak passwords, open ports, unnecessary services, default accounts, or incorrect permissions. Missing updates refer to any outdated or unsupported software or firmware that has not been patched with the latest security fixes or enhancements from the vendors2. Misconfiguration and missing updates are common sources of network vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, execute malicious code, cause denial of service, or escalate privileges on the network devices3.
Therefore, an IS auditor should expect to see misconfiguration and missing updates in a network vulnerability assessment. The other options are less relevant or incorrect because:
* B. Malicious software and spyware are not usually detected by a network vulnerability assessment, as they are more related to the content and behavior of the network traffic rather than the configuration and patch level of the network devices. Malicious software and spyware are programs that infect or monitor the network devices or their users for malicious purposes, such as stealing data, displaying ads, or performing remote commands. Malicious software and spyware can be detected by other security tools, such as antivirus software, firewalls, or intrusion detection systems4.
* C. Zero-day vulnerabilities are not usually detected by a network vulnerability assessment, as they are unknown or undisclosed vulnerabilities that have not been reported or patched by the vendors or the security community. Zero-day vulnerabilities are rare and difficult to discover, as they require advanced techniques and skills to exploit them. Zero-day vulnerabilities can be detected by other security tools, such as intrusion prevention systems, anomaly detection systems, or artificial intelligence systems5.
* D. Security design flaws are not usually detected by a network vulnerability assessment, as they are more related to the logic and functionality of the network rather than the configuration and patch level of the network devices. Security design flaws are errors or weaknesses in the network architecture, design, policies, or procedures that could compromise the security objectives of the network. Security design flaws can be detected by other security methods, such as security reviews, audits, or assessments6.
References: Network Vulnerability Assessment - ISACA, Network Vulnerability Scanning - NIST, Network Vulnerabilities - SANS, Malware - ISACA, Zero-Day Attacks - ISACA, Security Design Principles - NIST
Misconfiguration refers to any deviation from the recommended or best practice settings for the network devices, such as weak passwords, open ports, unnecessary services, default accounts, or incorrect permissions. Missing updates refer to any outdated or unsupported software or firmware that has not been patched with the latest security fixes or enhancements from the vendors2. Misconfiguration and missing updates are common sources of network vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, execute malicious code, cause denial of service, or escalate privileges on the network devices3.
Therefore, an IS auditor should expect to see misconfiguration and missing updates in a network vulnerability assessment. The other options are less relevant or incorrect because:
* B. Malicious software and spyware are not usually detected by a network vulnerability assessment, as they are more related to the content and behavior of the network traffic rather than the configuration and patch level of the network devices. Malicious software and spyware are programs that infect or monitor the network devices or their users for malicious purposes, such as stealing data, displaying ads, or performing remote commands. Malicious software and spyware can be detected by other security tools, such as antivirus software, firewalls, or intrusion detection systems4.
* C. Zero-day vulnerabilities are not usually detected by a network vulnerability assessment, as they are unknown or undisclosed vulnerabilities that have not been reported or patched by the vendors or the security community. Zero-day vulnerabilities are rare and difficult to discover, as they require advanced techniques and skills to exploit them. Zero-day vulnerabilities can be detected by other security tools, such as intrusion prevention systems, anomaly detection systems, or artificial intelligence systems5.
* D. Security design flaws are not usually detected by a network vulnerability assessment, as they are more related to the logic and functionality of the network rather than the configuration and patch level of the network devices. Security design flaws are errors or weaknesses in the network architecture, design, policies, or procedures that could compromise the security objectives of the network. Security design flaws can be detected by other security methods, such as security reviews, audits, or assessments6.
References: Network Vulnerability Assessment - ISACA, Network Vulnerability Scanning - NIST, Network Vulnerabilities - SANS, Malware - ISACA, Zero-Day Attacks - ISACA, Security Design Principles - NIST
Question 187
Which of the following protocol uses serial interface for communication between two computers in WAN technology?
Correct Answer: A
Explanation/Reference:
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol for communication between two computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer using a MODEM connected by phone line to a server.
For your exam you should know below information about WAN Technologies:
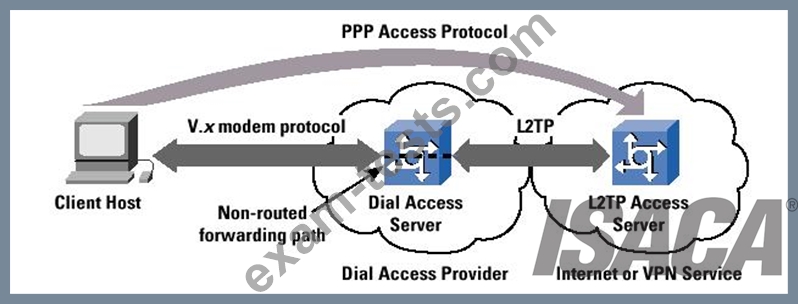
Point-to-point protocol
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol for communication between two computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer connected by phone line to a server. For example, your Internet server provider may provide you with a PPP connection so that the provider's server can respond to your requests, pass them on to the Internet, and forward your requested Internet responses back to you. PPP uses the Internet protocol (IP) (and is designed to handle others). It is sometimes considered a member of the TCP/IP suite of protocols. Relative to the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model, PPP provides layer 2 (data-link layer) service. Essentially, it packages your computer's TCP/IP packets and forwards them to the server where they can actually be put on the Internet.
PPP is a full-duplex protocol that can be used on various physical media, including twisted pair or fiber optic lines or satellite transmission. It uses a variation of High Speed Data Link Control (HDLC) for packet encapsulation.
PPP is usually preferred over the earlier de facto standard Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) because it can handle synchronous as well as asynchronous communication. PPP can share a line with other users and it has error detection that SLIP lacks. Where a choice is possible, PPP is preferred.
Point-to-point protocol
X.25
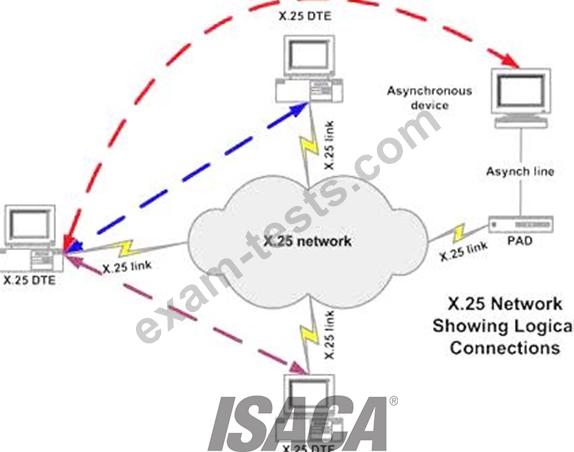
X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet switched wide area network (WAN) communication.
X.25 is a packet switching technology which uses carrier switch to provide connectivity for many different networks.
Subscribers are charged based on amount of bandwidth they use. Data are divided into 128 bytes and encapsulated in High Level Data Link Control (HDLC).
X.25 works at network and data link layer of an OSI model.
X.25
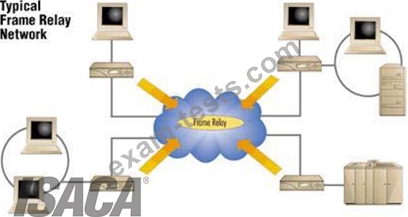
Frame Relay
Works on a packet switching
Operates at data link layer of an OSI model
Companies that pay more to ensure that a higher level of bandwidth will always be available, pay a committed information rate or CIR
Two main types of equipment's are used in Frame Relay
1. Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) - Usually a customer owned device that provides a connectivity between company's own network and the frame relay's network.
2. Data Circuit Terminal Equipment (DCE) - Service provider device that does the actual data transmission and switching in the frame relay cloud.
The Frame relay cloud is the collection of DCE that provides that provides switching and data communication functionality. Frame relay is any to any service.
Frame Relay
Integrated Service Digital Network
Enables data, voice and other types of traffic to travel over a medium in a digital manner previously used only for analog voice transmission.
Same copper telephone wire is used.
Provide digital point-to-point circuit switching medium.
ISDN
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
Uses Cell switching method
High speed network technology used for LAN, MAN and WAN
Like a frame relay it is connection oriented technology which creates and uses fixed channel Data are segmented into fixed size cell of 53 bytes
Some companies have replaces FDDI back-end with ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standards-approved technology for speeding up network traffic flow and making it easier to manage. MPLS involves setting up a specific path for a given sequence of packets, identified by a label put in each packet, thus saving the time needed for a router to look up the address to the next node to forward the packet to. MPLS is called multiprotocol because it works with the Internet Protocol (IP), Asynchronous Transport Mode (ATM), and frame relay network protocols. With reference to the standard model for a network (the Open Systems Interconnection, or OSI model), MPLS allows most packets to be forwarded at the Layer 2 (switching) level rather than at the Layer 3 (routing) level. In addition to moving traffic faster overall, MPLS makes it easy to manage a network for quality of service (QoS). For these reasons, the technique is expected to be readily adopted as networks begin to carry more and different mixtures of traffic.
MPLS
The following answers are incorrect:
X.25 - X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet switched wide area network (WAN) communication.X.25 is a packet switching technology which uses carrier switch to provide connectivity for many different networks.
Frame Relay - The Frame relay cloud is the collection of DCE that provides that provides switching and data communication functionality. Frame relay is any to any service.
ISDN -Enables data, voice and other types of traffic to travel over a medium in a digital manner previously used only for analog voice transmission. Same copper telephone wire is used. Provide digital point-to-point circuit switching medium.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 266
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol for communication between two computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer using a MODEM connected by phone line to a server.
For your exam you should know below information about WAN Technologies:
Point-to-point protocol
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol for communication between two computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer connected by phone line to a server. For example, your Internet server provider may provide you with a PPP connection so that the provider's server can respond to your requests, pass them on to the Internet, and forward your requested Internet responses back to you. PPP uses the Internet protocol (IP) (and is designed to handle others). It is sometimes considered a member of the TCP/IP suite of protocols. Relative to the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model, PPP provides layer 2 (data-link layer) service. Essentially, it packages your computer's TCP/IP packets and forwards them to the server where they can actually be put on the Internet.
PPP is a full-duplex protocol that can be used on various physical media, including twisted pair or fiber optic lines or satellite transmission. It uses a variation of High Speed Data Link Control (HDLC) for packet encapsulation.
PPP is usually preferred over the earlier de facto standard Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) because it can handle synchronous as well as asynchronous communication. PPP can share a line with other users and it has error detection that SLIP lacks. Where a choice is possible, PPP is preferred.
Point-to-point protocol

X.25
X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet switched wide area network (WAN) communication.
X.25 is a packet switching technology which uses carrier switch to provide connectivity for many different networks.
Subscribers are charged based on amount of bandwidth they use. Data are divided into 128 bytes and encapsulated in High Level Data Link Control (HDLC).
X.25 works at network and data link layer of an OSI model.

X.25
Frame Relay
Works on a packet switching
Operates at data link layer of an OSI model
Companies that pay more to ensure that a higher level of bandwidth will always be available, pay a committed information rate or CIR
Two main types of equipment's are used in Frame Relay
1. Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) - Usually a customer owned device that provides a connectivity between company's own network and the frame relay's network.
2. Data Circuit Terminal Equipment (DCE) - Service provider device that does the actual data transmission and switching in the frame relay cloud.
The Frame relay cloud is the collection of DCE that provides that provides switching and data communication functionality. Frame relay is any to any service.

Frame Relay
Integrated Service Digital Network
Enables data, voice and other types of traffic to travel over a medium in a digital manner previously used only for analog voice transmission.
Same copper telephone wire is used.
Provide digital point-to-point circuit switching medium.
ISDN

Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
Uses Cell switching method
High speed network technology used for LAN, MAN and WAN
Like a frame relay it is connection oriented technology which creates and uses fixed channel Data are segmented into fixed size cell of 53 bytes
Some companies have replaces FDDI back-end with ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standards-approved technology for speeding up network traffic flow and making it easier to manage. MPLS involves setting up a specific path for a given sequence of packets, identified by a label put in each packet, thus saving the time needed for a router to look up the address to the next node to forward the packet to. MPLS is called multiprotocol because it works with the Internet Protocol (IP), Asynchronous Transport Mode (ATM), and frame relay network protocols. With reference to the standard model for a network (the Open Systems Interconnection, or OSI model), MPLS allows most packets to be forwarded at the Layer 2 (switching) level rather than at the Layer 3 (routing) level. In addition to moving traffic faster overall, MPLS makes it easy to manage a network for quality of service (QoS). For these reasons, the technique is expected to be readily adopted as networks begin to carry more and different mixtures of traffic.
MPLS

The following answers are incorrect:
X.25 - X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet switched wide area network (WAN) communication.X.25 is a packet switching technology which uses carrier switch to provide connectivity for many different networks.
Frame Relay - The Frame relay cloud is the collection of DCE that provides that provides switching and data communication functionality. Frame relay is any to any service.
ISDN -Enables data, voice and other types of traffic to travel over a medium in a digital manner previously used only for analog voice transmission. Same copper telephone wire is used. Provide digital point-to-point circuit switching medium.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 266
Question 188
Which of the following should an IS auditor recommend be performed FIRST when evaluating potential enterprise resource planning (ERP) implementation vendors?
Correct Answer: A
Question 189
Which of the following is the MAIN responsibility of the IT steering committee?
Correct Answer: A
Explanation
This means that the IT steering committee is responsible for ensuring that the IT strategy aligns with and supports the business strategy, vision, and goals of the organization. The IT steering committee is also responsible for overseeing and approving major IT initiatives, projects, and investments, and allocating resources and priorities accordingly12.
Developing and assessing the IT security strategy (B) is not the main responsibility of the IT steering committee, but rather a specific aspect of the IT strategy that may be delegated to a subcommittee or a dedicated security function. The IT steering committee may provide guidance and oversight for the IT security strategy, but it is not directly involved in developing and assessing it12.
Implementing processes to integrate security with business objectives is not the main responsibility of the IT steering committee, but rather an operational task that may be performed by the IT management and staff. The IT steering committee may monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the security processes, but it is not directly involved in implementing them12.
Developing and implementing the secure system development framework (D) is not the main responsibility of the IT steering committee, but rather a technical task that may be performed by the IT developers and engineers. The IT steering committee may approve and endorse the secure system development framework, but it is not directly involved in developing and implementing it12.
This means that the IT steering committee is responsible for ensuring that the IT strategy aligns with and supports the business strategy, vision, and goals of the organization. The IT steering committee is also responsible for overseeing and approving major IT initiatives, projects, and investments, and allocating resources and priorities accordingly12.
Developing and assessing the IT security strategy (B) is not the main responsibility of the IT steering committee, but rather a specific aspect of the IT strategy that may be delegated to a subcommittee or a dedicated security function. The IT steering committee may provide guidance and oversight for the IT security strategy, but it is not directly involved in developing and assessing it12.
Implementing processes to integrate security with business objectives is not the main responsibility of the IT steering committee, but rather an operational task that may be performed by the IT management and staff. The IT steering committee may monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the security processes, but it is not directly involved in implementing them12.
Developing and implementing the secure system development framework (D) is not the main responsibility of the IT steering committee, but rather a technical task that may be performed by the IT developers and engineers. The IT steering committee may approve and endorse the secure system development framework, but it is not directly involved in developing and implementing it12.
Question 190
Which of the following exposures associated with the spooling of sensitive reports for offline printing should an IS auditor consider to be the MOST serious?
Correct Answer: C
Unless controlled, spooling for offline printing may enable additional copies to be printed. Print files are unlikely to be available for online reading by operators. Data on spool files are no easier to amend without authority than any other file. There is usually a lesser threat of unauthorized access to sensitive reports in the event of a system failure.
- Other Version
- 4568ISACA.CISA.v2025-05-24.q773
- 4136ISACA.CISA.v2023-10-02.q715
- 3738ISACA.CISA.v2023-03-29.q119
- 2387ISACA.CISA.v2023-02-09.q181
- 1498ISACA.CISA.v2023-02-06.q107
- 3051ISACA.CISA.v2022-08-28.q129
- 4218ISACA.CISA.v2022-02-25.q148
- 126ISACA.Actualtestpdf.CISA.v2021-11-13.by.sarah.721q.pdf
- 5623ISACA.CISA.v2021-11-11.q194
- 8820ISACA.CISA.v2021-10-08.q198
- 9797ISACA.CISA.v2021-09-28.q199
- 12254ISACA.CISA.v2021-09-11.q201
- Latest Upload
- 105OCEG.GRCP.v2025-09-11.q211
- 104HP.HPE0-V27.v2025-09-11.q78
- 118Oracle.1Z0-1057-23.v2025-09-10.q47
- 151Google.Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer.v2025-09-09.q179
- 131SAP.C-S4EWM-2023.v2025-09-08.q83
- 165TheSecOpsGroup.CNSP.v2025-09-08.q20
- 223CFAInstitute.ESG-Investing.v2025-09-08.q173
- 169PECB.ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Implementer.v2025-09-06.q132
- 150Salesforce.Data-Architect.v2025-09-05.q216
- 144Adobe.AD0-E605.v2025-09-05.q50
[×]
Download PDF File
Enter your email address to download ISACA.CISA.v2024-10-22.q310 Practice Test

