- Home
- Cisco Certification
- 350-701 Exam
- Cisco.350-701.v2022-02-02.q204 Practice Test
Question 131
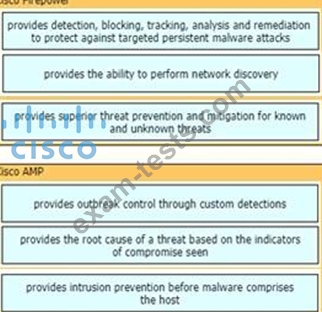
Drag and drop the capabilities of Cisco Firepower versus Cisco AMP from the left into the appropriate category on the right.


Correct Answer:

Explanation
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/ngips/datasheet-c78-742472.html
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/firepower/60/configuration/guide/fpmc-config-guide-v60/Refere
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/enterprise-networks/advanced-malware-protection/solution-ov
Question 132
What is a feature of the open platform capabilities of Cisco DNA Center?
Correct Answer: A
Question 133
An engineer has been tasked with configuring a Cisco FTD to analyze protocol fields and detect anomalies in the traffic from industrial systems. What must be done to meet these requirements?
Correct Answer: A
Explanation The Modbus, DNP3, and CIP SCADA preprocessors detect traffic anomalies and provide data to intrusion rules. Therefore in this question only answer A or answer C is correct. The DNP3 preprocessor detects anomalies in DNP3 traffic and decodes the DNP3 protocol for processing by the rules engine, which uses DNP3 keywords to access certain protocol fields. The Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) is a widely used application protocol that supports industrial automation applications. EtherNet/IP is an implementation of CIP that is used on Ethernet-based networks.The CIP preprocessor detects CIP and ENIP traffic running on TCP or UDP and sends it to the intrusion rules engine. You can use CIP and ENIP keywords in custom intrusion rules to detect attacks in CIP and ENIP traffic. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/firepower/630/configuration/guide/fpmc-configguide-v63/scada_preprocessors.html Both DNP3 and CIP preprocessors can be used to detect traffic anomalies but we choose CIP as it is widely used in industrial applications. Note: + An intrusion rule is a specified set of keywords and arguments that the system uses to detect attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in your network. As the system analyzes network traffic, it compares packets against the conditions specified in each rule, and triggers the rule if the data packet meets all the conditions specified in the rule. + Preprocessor rules, which are rules associated with preprocessors and packet decoder detection options in the network analysis policy. Most preprocessor rules are disabled by default.
The Modbus, DNP3, and CIP SCADA preprocessors detect traffic anomalies and provide data to intrusion rules. Therefore in this question only answer A or answer C is correct.
The DNP3 preprocessor detects anomalies in DNP3 traffic and decodes the DNP3 protocol for processing by the rules engine, which uses DNP3 keywords to access certain protocol fields.
The Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) is a widely used application protocol that supports industrial automation applications. EtherNet/IP is an implementation of CIP that is used on Ethernet-based networks.The CIP preprocessor detects CIP and ENIP traffic running on TCP or UDP and sends it to the intrusion rules engine.
You can use CIP and ENIP keywords in custom intrusion rules to detect attacks in CIP and ENIP traffic.
Reference:
Both DNP3 and CIP preprocessors can be used to detect traffic anomalies but we choose CIP as it is widely used in industrial applications.
Note:
Explanation The Modbus, DNP3, and CIP SCADA preprocessors detect traffic anomalies and provide data to intrusion rules. Therefore in this question only answer A or answer C is correct. The DNP3 preprocessor detects anomalies in DNP3 traffic and decodes the DNP3 protocol for processing by the rules engine, which uses DNP3 keywords to access certain protocol fields. The Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) is a widely used application protocol that supports industrial automation applications. EtherNet/IP is an implementation of CIP that is used on Ethernet-based networks.The CIP preprocessor detects CIP and ENIP traffic running on TCP or UDP and sends it to the intrusion rules engine. You can use CIP and ENIP keywords in custom intrusion rules to detect attacks in CIP and ENIP traffic. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/firepower/630/configuration/guide/fpmc-configguide-v63/scada_preprocessors.html Both DNP3 and CIP preprocessors can be used to detect traffic anomalies but we choose CIP as it is widely used in industrial applications. Note: + An intrusion rule is a specified set of keywords and arguments that the system uses to detect attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in your network. As the system analyzes network traffic, it compares packets against the conditions specified in each rule, and triggers the rule if the data packet meets all the conditions specified in the rule. + Preprocessor rules, which are rules associated with preprocessors and packet decoder detection options in the network analysis policy. Most preprocessor rules are disabled by default.
The Modbus, DNP3, and CIP SCADA preprocessors detect traffic anomalies and provide data to intrusion rules. Therefore in this question only answer A or answer C is correct.
The DNP3 preprocessor detects anomalies in DNP3 traffic and decodes the DNP3 protocol for processing by the rules engine, which uses DNP3 keywords to access certain protocol fields.
The Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) is a widely used application protocol that supports industrial automation applications. EtherNet/IP is an implementation of CIP that is used on Ethernet-based networks.The CIP preprocessor detects CIP and ENIP traffic running on TCP or UDP and sends it to the intrusion rules engine.
You can use CIP and ENIP keywords in custom intrusion rules to detect attacks in CIP and ENIP traffic.
Reference:
Both DNP3 and CIP preprocessors can be used to detect traffic anomalies but we choose CIP as it is widely used in industrial applications.
Note:
Explanation The Modbus, DNP3, and CIP SCADA preprocessors detect traffic anomalies and provide data to intrusion rules. Therefore in this question only answer A or answer C is correct. The DNP3 preprocessor detects anomalies in DNP3 traffic and decodes the DNP3 protocol for processing by the rules engine, which uses DNP3 keywords to access certain protocol fields. The Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) is a widely used application protocol that supports industrial automation applications. EtherNet/IP is an implementation of CIP that is used on Ethernet-based networks.The CIP preprocessor detects CIP and ENIP traffic running on TCP or UDP and sends it to the intrusion rules engine. You can use CIP and ENIP keywords in custom intrusion rules to detect attacks in CIP and ENIP traffic. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/firepower/630/configuration/guide/fpmc-configguide-v63/scada_preprocessors.html Both DNP3 and CIP preprocessors can be used to detect traffic anomalies but we choose CIP as it is widely used in industrial applications. Note: + An intrusion rule is a specified set of keywords and arguments that the system uses to detect attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in your network. As the system analyzes network traffic, it compares packets against the conditions specified in each rule, and triggers the rule if the data packet meets all the conditions specified in the rule. + Preprocessor rules, which are rules associated with preprocessors and packet decoder detection options in the network analysis policy. Most preprocessor rules are disabled by default.
Question 134
What are two benefits of Flexible NetFlow records? (Choose two)
Correct Answer: A,C
NetFlow is typically used for several key customer applications, including the following:
...
Billing and accounting. NetFlow data provides fine-grained metering (for instance, flow data includes details such as IP addresses, packet and byte counts, time stamps, type of service (ToS), and application ports) for highly flexible and detailed resource utilization accounting. Service providers may use the information for billing based on time of day, bandwidth usage, application usage, quality of service, and so on. Enterprise customers may use the information for departmental charge back or cost allocation for resource utilization.
NetFlow is typically used for several key customer applications, including the following:
...
Billing and accounting. NetFlow data provides fine-grained metering (for instance, flow data includes details such as IP addresses, packet and byte counts, time stamps, type of service (ToS), and application ports) for highly flexible and detailed resource utilization accounting. Service providers may use the information for billing based on time of day, bandwidth usage, application usage, quality of service, and so on. Enterprise customers may use the information for departmental charge back or cost allocation for resource utilization.
Reference:
If the predefined Flexible NetFlow records are not suitable for your traffic requirements, you can create a userdefined (custom) record using the Flexible NetFlow collect and match commands. Before you can create a customized record, you must decide the criteria that you are going to use for the key and nonkey fields.
cust_fnflow_rec_mon_external_docbase_0900e4b18055d0d2_4container_external_docbase_0900e4b181b413 d9.html#wp1057997 Note: Traditional NetFlow allows us to monitor from Layer 2 to 4 but Flexible NetFlow goes beyond these layers.
NetFlow is typically used for several key customer applications, including the following:
...
Billing and accounting. NetFlow data provides fine-grained metering (for instance, flow data includes details such as IP addresses, packet and byte counts, time stamps, type of service (ToS), and application ports) for highly flexible and detailed resource utilization accounting. Service providers may use the information for billing based on time of day, bandwidth usage, application usage, quality of service, and so on. Enterprise customers may use the information for departmental charge back or cost allocation for resource utilization.
If the predefined Flexible NetFlow records are not suitable for your traffic requirements, you can create a userdefined (custom) record using the Flexible NetFlow collect and match commands. Before you can create a customized record, you must decide the criteria that you are going to use for the key and nonkey fields.
cust_fnflow_rec_mon_external_docbase_0900e4b18055d0d2_4container_external_docbase_0900e4b181b413 d9.html#wp1057997 Note: Traditional NetFlow allows us to monitor from Layer 2 to 4 but Flexible NetFlow goes beyond these If the predefined Flexible NetFlow records are not suitable for your traffic requirements, you can create a userdefined (custom) record using the Flexible NetFlow collect and match commands. Before you can create a customized record, you must decide the criteria that you are going to use for the key and nonkey fields.
cust_fnflow_rec_mon_external_docbase_0900e4b18055d0d2_4container_external_docbase_0900e4b181b413 d9.html#wp1057997 Note: Traditional NetFlow allows us to monitor from Layer 2 to 4 but Flexible NetFlow goes beyond these layers.
...
Billing and accounting. NetFlow data provides fine-grained metering (for instance, flow data includes details such as IP addresses, packet and byte counts, time stamps, type of service (ToS), and application ports) for highly flexible and detailed resource utilization accounting. Service providers may use the information for billing based on time of day, bandwidth usage, application usage, quality of service, and so on. Enterprise customers may use the information for departmental charge back or cost allocation for resource utilization.
NetFlow is typically used for several key customer applications, including the following:
...
Billing and accounting. NetFlow data provides fine-grained metering (for instance, flow data includes details such as IP addresses, packet and byte counts, time stamps, type of service (ToS), and application ports) for highly flexible and detailed resource utilization accounting. Service providers may use the information for billing based on time of day, bandwidth usage, application usage, quality of service, and so on. Enterprise customers may use the information for departmental charge back or cost allocation for resource utilization.
Reference:
If the predefined Flexible NetFlow records are not suitable for your traffic requirements, you can create a userdefined (custom) record using the Flexible NetFlow collect and match commands. Before you can create a customized record, you must decide the criteria that you are going to use for the key and nonkey fields.
cust_fnflow_rec_mon_external_docbase_0900e4b18055d0d2_4container_external_docbase_0900e4b181b413 d9.html#wp1057997 Note: Traditional NetFlow allows us to monitor from Layer 2 to 4 but Flexible NetFlow goes beyond these layers.
NetFlow is typically used for several key customer applications, including the following:
...
Billing and accounting. NetFlow data provides fine-grained metering (for instance, flow data includes details such as IP addresses, packet and byte counts, time stamps, type of service (ToS), and application ports) for highly flexible and detailed resource utilization accounting. Service providers may use the information for billing based on time of day, bandwidth usage, application usage, quality of service, and so on. Enterprise customers may use the information for departmental charge back or cost allocation for resource utilization.
If the predefined Flexible NetFlow records are not suitable for your traffic requirements, you can create a userdefined (custom) record using the Flexible NetFlow collect and match commands. Before you can create a customized record, you must decide the criteria that you are going to use for the key and nonkey fields.
cust_fnflow_rec_mon_external_docbase_0900e4b18055d0d2_4container_external_docbase_0900e4b181b413 d9.html#wp1057997 Note: Traditional NetFlow allows us to monitor from Layer 2 to 4 but Flexible NetFlow goes beyond these If the predefined Flexible NetFlow records are not suitable for your traffic requirements, you can create a userdefined (custom) record using the Flexible NetFlow collect and match commands. Before you can create a customized record, you must decide the criteria that you are going to use for the key and nonkey fields.
cust_fnflow_rec_mon_external_docbase_0900e4b18055d0d2_4container_external_docbase_0900e4b181b413 d9.html#wp1057997 Note: Traditional NetFlow allows us to monitor from Layer 2 to 4 but Flexible NetFlow goes beyond these layers.
Question 135
Where are individual sites specified to be blacklisted in Cisco Umbrella?
Correct Answer: D
A destination list is a list of internet destinations that can be blocked or allowed based on the administrative preferences for the policies applied to the identities within your organization. A destination is an IP address (IPv4), URL, or fully qualified domain name. You can add a destination list to Umbrella at any time; however, a destination list does not come into use until it is added to a policy.
A destination list is a list of internet destinations that can be blocked or allowed based on the administrative preferences for the policies applied to the identities within your organization. A destination is an IP address (IPv4), URL, or fully qualified domain name. You can add a destination list to Umbrella at any time; however, a destination list does not come into use until it is added to a policy.
Reference:
A destination list is a list of internet destinations that can be blocked or allowed based on the administrative preferences for the policies applied to the identities within your organization. A destination is an IP address (IPv4), URL, or fully qualified domain name. You can add a destination list to Umbrella at any time; however, a destination list does not come into use until it is added to a policy.
A destination list is a list of internet destinations that can be blocked or allowed based on the administrative preferences for the policies applied to the identities within your organization. A destination is an IP address (IPv4), URL, or fully qualified domain name. You can add a destination list to Umbrella at any time; however, a destination list does not come into use until it is added to a policy.
Reference:
A destination list is a list of internet destinations that can be blocked or allowed based on the administrative preferences for the policies applied to the identities within your organization. A destination is an IP address (IPv4), URL, or fully qualified domain name. You can add a destination list to Umbrella at any time; however, a destination list does not come into use until it is added to a policy.
- Other Version
- 466Cisco.350-701.v2025-06-19.q238
- 753Cisco.350-701.v2024-12-18.q472
- 2171Cisco.350-701.v2023-08-01.q405
- 2559Cisco.350-701.v2023-05-04.q372
- 1948Cisco.350-701.v2023-03-16.q218
- 6693Cisco.350-701.v2022-10-19.q571
- 6646Cisco.350-701.v2022-07-08.q453
- 116Cisco.Prepawaypdf.350-701.v2021-12-15.by.ellen.316q.pdf
- Latest Upload
- 106OCEG.GRCP.v2025-09-11.q211
- 106HP.HPE0-V27.v2025-09-11.q78
- 121Oracle.1Z0-1057-23.v2025-09-10.q47
- 157Google.Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer.v2025-09-09.q179
- 136SAP.C-S4EWM-2023.v2025-09-08.q83
- 171TheSecOpsGroup.CNSP.v2025-09-08.q20
- 237CFAInstitute.ESG-Investing.v2025-09-08.q173
- 220PECB.ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Implementer.v2025-09-06.q132
- 155Salesforce.Data-Architect.v2025-09-05.q216
- 149Adobe.AD0-E605.v2025-09-05.q50
[×]
Download PDF File
Enter your email address to download Cisco.350-701.v2022-02-02.q204 Practice Test

