- Home
- Cisco Certification
- 350-701 Exam
- Cisco.350-701.v2022-10-19.q571 Practice Test
Question 391
Due to a traffic storm on the network, two interfaces were error-disabled, and both interfaces sent SNMP traps.
Which two actions must be taken to ensure that interfaces are put back into service? (Choose two)
Which two actions must be taken to ensure that interfaces are put back into service? (Choose two)
Correct Answer: C,E
Explanation
You can also bring up the port by using these commands:
+ The "shutdown" interface configuration command followed by the "no shutdown" interface configuration command restarts the disabled port.
+ The "errdisable recovery cause ..." global configuration command enables the timer to automatically recover error-disabled state, and the "errdisable recovery interval interval" global configuration command specifies the time to recover error-disabled state.
You can also bring up the port by using these commands:
+ The "shutdown" interface configuration command followed by the "no shutdown" interface configuration command restarts the disabled port.
+ The "errdisable recovery cause ..." global configuration command enables the timer to automatically recover error-disabled state, and the "errdisable recovery interval interval" global configuration command specifies the time to recover error-disabled state.
Question 392
An organization has a Cisco ESA set up with policies and would like to customize the action assigned for violations. The organization wants a copy of the message to be delivered with a message added to flag it as a DLP violation. Which actions must be performed in order to provide this capability?
Correct Answer: D
Explanation Explanation You specify primary and secondary actions that the appliance will take when it detects a possible DLP violation in an outgoing message. Different actions can be assigned for different violation types and severities. Primary actions include: - Deliver - Drop - Quarantine Secondary actions include: - Sending a copy to a policy quarantine if you choose to deliver the message. The copy is a perfect clone of the original, including the Message ID. Quarantining a copy allows you to test the DLP system before deployment in addition to providing another way to monitor DLP violations. When you release the copy from the quarantine, the appliance delivers the copy to the recipient, who will have already received the original message. - Encrypting messages. The appliance only encrypts the message body. It does not encrypt the message headers. - Altering the subject header of messages containing a DLP violation. - Adding disclaimer text to messages. - Sending messages to an alternate destination mailhost. - Sending copies (bcc) of messages to other recipients. (For example, you could copy messages with critical DLP violations to a compliance officer's mailbox for examination.) - Sending a DLP violation notification message to the sender or other contacts, such as a manager or DLP compliance officer. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/esa/esa12-0/user_guide/ b_ESA_Admin_Guide_12_0/b_ESA_Admin_Guide_chapter_010001.html Explanation You specify primary and secondary actions that the appliance will take when it detects a possible DLP violation in an outgoing message. Different actions can be assigned for different violation types and severities.
Primary actions include:
- Deliver
- Drop
- Quarantine
Secondary actions include:
- Sending a copy to a policy quarantine if you choose to deliver the message. The copy is a perfect clone of the original, including the Message ID. Quarantining a copy allows you to test the DLP system before deployment in addition to providing another way to monitor DLP violations. When you release the copy from the quarantine, the appliance delivers the copy to the recipient, who will have already received the original message.
- Encrypting messages. The appliance only encrypts the message body. It does not encrypt the message headers.
- Altering the subject header of messages containing a DLP violation.
- Adding disclaimer text to messages.
- Sending messages to an alternate destination mailhost.
- Sending copies (bcc) of messages to other recipients. (For example, you could copy messages with critical DLP violations to a compliance officer's mailbox for examination.)
- Sending a DLP violation notification message to the sender or other contacts, such as a manager or DLP compliance officer.
Reference:
Explanation Explanation You specify primary and secondary actions that the appliance will take when it detects a possible DLP violation in an outgoing message. Different actions can be assigned for different violation types and severities. Primary actions include: - Deliver - Drop - Quarantine Secondary actions include: - Sending a copy to a policy quarantine if you choose to deliver the message. The copy is a perfect clone of the original, including the Message ID. Quarantining a copy allows you to test the DLP system before deployment in addition to providing another way to monitor DLP violations. When you release the copy from the quarantine, the appliance delivers the copy to the recipient, who will have already received the original message. - Encrypting messages. The appliance only encrypts the message body. It does not encrypt the message headers. - Altering the subject header of messages containing a DLP violation. - Adding disclaimer text to messages. - Sending messages to an alternate destination mailhost. - Sending copies (bcc) of messages to other recipients. (For example, you could copy messages with critical DLP violations to a compliance officer's mailbox for examination.) - Sending a DLP violation notification message to the sender or other contacts, such as a manager or DLP compliance officer. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/esa/esa12-0/user_guide/ b_ESA_Admin_Guide_12_0/b_ESA_Admin_Guide_chapter_010001.html
Primary actions include:
- Deliver
- Drop
- Quarantine
Secondary actions include:
- Sending a copy to a policy quarantine if you choose to deliver the message. The copy is a perfect clone of the original, including the Message ID. Quarantining a copy allows you to test the DLP system before deployment in addition to providing another way to monitor DLP violations. When you release the copy from the quarantine, the appliance delivers the copy to the recipient, who will have already received the original message.
- Encrypting messages. The appliance only encrypts the message body. It does not encrypt the message headers.
- Altering the subject header of messages containing a DLP violation.
- Adding disclaimer text to messages.
- Sending messages to an alternate destination mailhost.
- Sending copies (bcc) of messages to other recipients. (For example, you could copy messages with critical DLP violations to a compliance officer's mailbox for examination.)
- Sending a DLP violation notification message to the sender or other contacts, such as a manager or DLP compliance officer.
Reference:
Explanation Explanation You specify primary and secondary actions that the appliance will take when it detects a possible DLP violation in an outgoing message. Different actions can be assigned for different violation types and severities. Primary actions include: - Deliver - Drop - Quarantine Secondary actions include: - Sending a copy to a policy quarantine if you choose to deliver the message. The copy is a perfect clone of the original, including the Message ID. Quarantining a copy allows you to test the DLP system before deployment in addition to providing another way to monitor DLP violations. When you release the copy from the quarantine, the appliance delivers the copy to the recipient, who will have already received the original message. - Encrypting messages. The appliance only encrypts the message body. It does not encrypt the message headers. - Altering the subject header of messages containing a DLP violation. - Adding disclaimer text to messages. - Sending messages to an alternate destination mailhost. - Sending copies (bcc) of messages to other recipients. (For example, you could copy messages with critical DLP violations to a compliance officer's mailbox for examination.) - Sending a DLP violation notification message to the sender or other contacts, such as a manager or DLP compliance officer. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/esa/esa12-0/user_guide/ b_ESA_Admin_Guide_12_0/b_ESA_Admin_Guide_chapter_010001.html
Question 393
Which service allows a user export application usage and performance statistics with Cisco Application Visibility and control?
Correct Answer: B
Explanation
Application Visibility and control (AVC) supports NetFlow to export application usage and performance statistics. This data can be used for analytics, billing, and security policies.
Application Visibility and control (AVC) supports NetFlow to export application usage and performance statistics. This data can be used for analytics, billing, and security policies.
Question 394
How does DNS Tunneling exfiltrate data?
Correct Answer: A
Explanation
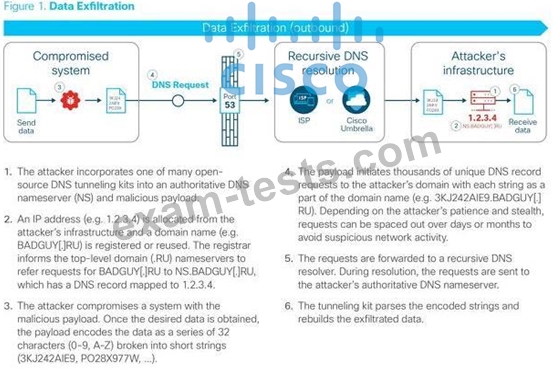

Question 395
What are two features of NetFlow flow monitoring? (Choose two)
Correct Answer: A,E
The following are restrictions for Flexible NetFlow:
+ Traditional NetFlow (TNF) accounting is not supported.
+ Flexible NetFlow v5 export format is not supported, only NetFlow v9 export format is supported.
+ Both ingress and egress NetFlow accounting is supported.
+ Microflow policing feature shares the NetFlow hardware resource with FNF.
+ Only one flow monitor per interface and per direction is supported.
The following are restrictions for Flexible NetFlow:
+ Traditional NetFlow (TNF) accounting is not supported.
+ Flexible NetFlow v5 export format is not supported, only NetFlow v9 export format is supported.
+ Both ingress and egress NetFlow accounting is supported.
+ Microflow policing feature shares the NetFlow hardware resource with FNF.
+ Only one flow monitor per interface and per direction is supported.
Reference:
consolidated_guide/b_consolidated_3850_3se_cg_chapter_011010.html
When configuring NetFlow, follow these guidelines and restrictions:
+ Except in PFC3A mode, NetFlow supports bridged IP traffic. PFC3A mode does not support NetFlow bridged IP traffic.
+ NetFlow supports multicast IP traffic.
The Flexible NetFlow - MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets that arrive on a router as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets and are transmitted as IP packets. This feature allows you to capture the MPLS VPN IP flows that are traveling through the service provider backbone from one site of a VPN to another site of the same VPN The following are restrictions for Flexible NetFlow:
+ Traditional NetFlow (TNF) accounting is not supported.
+ Flexible NetFlow v5 export format is not supported, only NetFlow v9 export format is supported.
+ Both ingress and egress NetFlow accounting is supported.
+ Microflow policing feature shares the NetFlow hardware resource with FNF.
+ Only one flow monitor per interface and per direction is supported.
consolidated_guide/b_consolidated_3850_3se_cg_chapter_011010.html
When configuring NetFlow, follow these guidelines and restrictions:
+ Except in PFC3A mode, NetFlow supports bridged IP traffic. PFC3A mode does not support NetFlow bridged IP traffic.
+ NetFlow supports multicast IP traffic.
The Flexible NetFlow - MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets that arrive on a router as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets and are transmitted as IP packets. This feature allows you to capture the MPLS VPN IP flows that are traveling through the service provider backbone from one site of a VPN to another site of the same VPN consolidated_guide/b_consolidated_3850_3se_cg_chapter_011010.html When configuring NetFlow, follow these guidelines and restrictions:
+ Except in PFC3A mode, NetFlow supports bridged IP traffic. PFC3A mode does not support NetFlow bridged IP traffic.
+ NetFlow supports multicast IP traffic.
The Flexible NetFlow - MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets that arrive on a router as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets and are transmitted as IP packets. This feature allows you to capture the MPLS VPN IP flows that are traveling through the service provider backbone from one site of a VPN to another site of the same VPN
+ Traditional NetFlow (TNF) accounting is not supported.
+ Flexible NetFlow v5 export format is not supported, only NetFlow v9 export format is supported.
+ Both ingress and egress NetFlow accounting is supported.
+ Microflow policing feature shares the NetFlow hardware resource with FNF.
+ Only one flow monitor per interface and per direction is supported.
The following are restrictions for Flexible NetFlow:
+ Traditional NetFlow (TNF) accounting is not supported.
+ Flexible NetFlow v5 export format is not supported, only NetFlow v9 export format is supported.
+ Both ingress and egress NetFlow accounting is supported.
+ Microflow policing feature shares the NetFlow hardware resource with FNF.
+ Only one flow monitor per interface and per direction is supported.
Reference:
consolidated_guide/b_consolidated_3850_3se_cg_chapter_011010.html
When configuring NetFlow, follow these guidelines and restrictions:
+ Except in PFC3A mode, NetFlow supports bridged IP traffic. PFC3A mode does not support NetFlow bridged IP traffic.
+ NetFlow supports multicast IP traffic.
The Flexible NetFlow - MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets that arrive on a router as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets and are transmitted as IP packets. This feature allows you to capture the MPLS VPN IP flows that are traveling through the service provider backbone from one site of a VPN to another site of the same VPN The following are restrictions for Flexible NetFlow:
+ Traditional NetFlow (TNF) accounting is not supported.
+ Flexible NetFlow v5 export format is not supported, only NetFlow v9 export format is supported.
+ Both ingress and egress NetFlow accounting is supported.
+ Microflow policing feature shares the NetFlow hardware resource with FNF.
+ Only one flow monitor per interface and per direction is supported.
consolidated_guide/b_consolidated_3850_3se_cg_chapter_011010.html
When configuring NetFlow, follow these guidelines and restrictions:
+ Except in PFC3A mode, NetFlow supports bridged IP traffic. PFC3A mode does not support NetFlow bridged IP traffic.
+ NetFlow supports multicast IP traffic.
The Flexible NetFlow - MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets that arrive on a router as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets and are transmitted as IP packets. This feature allows you to capture the MPLS VPN IP flows that are traveling through the service provider backbone from one site of a VPN to another site of the same VPN consolidated_guide/b_consolidated_3850_3se_cg_chapter_011010.html When configuring NetFlow, follow these guidelines and restrictions:
+ Except in PFC3A mode, NetFlow supports bridged IP traffic. PFC3A mode does not support NetFlow bridged IP traffic.
+ NetFlow supports multicast IP traffic.
The Flexible NetFlow - MPLS Egress NetFlow feature allows you to capture IP flow information for packets that arrive on a router as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets and are transmitted as IP packets. This feature allows you to capture the MPLS VPN IP flows that are traveling through the service provider backbone from one site of a VPN to another site of the same VPN
- Other Version
- 1537Cisco.350-701.v2025-10-04.q562
- 1078Cisco.350-701.v2025-06-19.q238
- 1568Cisco.350-701.v2024-12-18.q472
- 2735Cisco.350-701.v2023-08-01.q405
- 3451Cisco.350-701.v2023-05-04.q372
- 2368Cisco.350-701.v2023-03-16.q218
- 7278Cisco.350-701.v2022-07-08.q453
- 4202Cisco.350-701.v2022-02-02.q204
- 116Cisco.Prepawaypdf.350-701.v2021-12-15.by.ellen.316q.pdf
- Latest Upload
- 115EC-COUNCIL.312-76.v2026-01-03.q103
- 116PaloAltoNetworks.PSE-Cortex-Pro-24.v2026-01-03.q62
- 107MedicalTests.AAPC-CPC.v2026-01-03.q50
- 114SAP.C_S4CPB_2502.v2026-01-03.q43
- 129USGBC.LEED-AP-Homes.v2026-01-02.q36
- 115SAP.C-THR94-2505.v2026-01-02.q29
- 137MedicalProfessional.CHFM.v2026-01-01.q37
- 116SAP.C-BCSPM-2502.v2026-01-01.q9
- 118Microsoft.MB-335.v2026-01-01.q142
- 124SAP.C_THR70_2505.v2026-01-01.q55
[×]
Download PDF File
Enter your email address to download Cisco.350-701.v2022-10-19.q571 Practice Test

