- Home
- PECB Certification
- ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Auditor-CN Exam
- PECB.ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Auditor-CN.v2026-01-16.q166 Practice Test
Question 91
您是審計團隊負責人,對一家線上保險機構進行第三方審計。舞台期間
1,您發現組織採取了非常謹慎的風險方法,並將 ISO/IEC 27001:2022 附錄 A 中的所有資訊安全控制措施納入其適用性聲明中。
在第二階段審核期間,您的審核團隊發現沒有證據顯示實施了適用性聲明摘錄中顯示的三項控制措施(5.3 職責分離、6.1 篩選、7.12 佈線安全)。未找到風險處理方案。
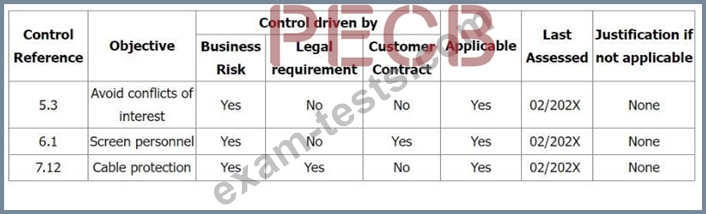
選擇三個選項,說明您希望受審核方針對 ISO/IEC 27001:2022 第 6.1.3.e 條的不符合項所採取的措施。
1,您發現組織採取了非常謹慎的風險方法,並將 ISO/IEC 27001:2022 附錄 A 中的所有資訊安全控制措施納入其適用性聲明中。
在第二階段審核期間,您的審核團隊發現沒有證據顯示實施了適用性聲明摘錄中顯示的三項控制措施(5.3 職責分離、6.1 篩選、7.12 佈線安全)。未找到風險處理方案。

選擇三個選項,說明您希望受審核方針對 ISO/IEC 27001:2022 第 6.1.3.e 條的不符合項所採取的措施。
Correct Answer: C,F,G
According to the PECB Candidate Handbook for ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor, the auditee should take the following actions in response to a nonconformity against clause 6.1.3.e of ISO/IEC 27001:20221:
* Implement the appropriate risk treatment for each of the applicable controls, as this is the main requirement of clause 6.1.3.e and the objective of the risk treatment process2.
* Revise the relevant content in the Statement of Applicability to justify their exclusion, as this is the expected output of the risk treatment process and the evidence of the risk-based decisions3.
* Revisit the risk assessment process relating to the three controls, as this is the input for the risk treatment process and the source of identifying the risks and the controls4.
The other options are not correct because:
* Allocating responsibility for producing evidence to prove to auditors that the controls are implemented is not a valid action, as the audit team already found that there was no evidence of the implementation of the three controls.
* Compiling plans for the periodic assessment of the risks associated with the controls is not a valid action, as this is part of the risk monitoring and review process, not the risk treatment process5.
* Incorporating written procedures for the controls into the organisation's Security Manual is not a valid action, as this is part of the documentation and operation of the ISMS, not the risk treatment process.
* Removing the three controls from the Statement of Applicability is not a valid action, as this is not a sufficient justification for their exclusion and does not reflect the risk treatment process.
* Undertaking a survey of customers to find out if the controls are needed by them is not a valid action, as this is not a relevant criterion for the risk assessment and treatment process, which should be based on the organisation's own context and objectives.
References: 1: PECB Candidate Handbook for ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor, page 36, section 4.5.22: ISO
/IEC 27001:2022, clause 6.1.3.e3: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 6.1.3.f4: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 6.1.25:
ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 6.2. : ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 7.5 and 8. : ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause
6.1.3.d. : ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 4.1 and 4.2.
* Implement the appropriate risk treatment for each of the applicable controls, as this is the main requirement of clause 6.1.3.e and the objective of the risk treatment process2.
* Revise the relevant content in the Statement of Applicability to justify their exclusion, as this is the expected output of the risk treatment process and the evidence of the risk-based decisions3.
* Revisit the risk assessment process relating to the three controls, as this is the input for the risk treatment process and the source of identifying the risks and the controls4.
The other options are not correct because:
* Allocating responsibility for producing evidence to prove to auditors that the controls are implemented is not a valid action, as the audit team already found that there was no evidence of the implementation of the three controls.
* Compiling plans for the periodic assessment of the risks associated with the controls is not a valid action, as this is part of the risk monitoring and review process, not the risk treatment process5.
* Incorporating written procedures for the controls into the organisation's Security Manual is not a valid action, as this is part of the documentation and operation of the ISMS, not the risk treatment process.
* Removing the three controls from the Statement of Applicability is not a valid action, as this is not a sufficient justification for their exclusion and does not reflect the risk treatment process.
* Undertaking a survey of customers to find out if the controls are needed by them is not a valid action, as this is not a relevant criterion for the risk assessment and treatment process, which should be based on the organisation's own context and objectives.
References: 1: PECB Candidate Handbook for ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor, page 36, section 4.5.22: ISO
/IEC 27001:2022, clause 6.1.3.e3: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 6.1.3.f4: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 6.1.25:
ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 6.2. : ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 7.5 and 8. : ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause
6.1.3.d. : ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 4.1 and 4.2.
Question 92
在定義以下內容時,評估與不合格和不遵守法律和合約要求相關的成本:
Correct Answer: A
Materiality in the context of an audit involves assessing what level of nonconformities or failures, including those related to legal and contractual compliance, would be significant enough to affect the audit conclusions.
Costs related to these issues are considered when determining materiality.
References: ISO 19011:2018, Guidelines for auditing management systems
Costs related to these issues are considered when determining materiality.
References: ISO 19011:2018, Guidelines for auditing management systems
Question 93
以下是「誠信」的目的,這是資訊安全的基本組成部分之一
Correct Answer: B
Integrity is one of the basic components of information security, along with confidentiality and availability.
Integrity means that information is safeguarded from unauthorized or accidental changes that could affect its accuracy and completeness. Integrity ensures that information is reliable and trustworthy3. References: ISO
/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor Training Course - BSI
Integrity means that information is safeguarded from unauthorized or accidental changes that could affect its accuracy and completeness. Integrity ensures that information is reliable and trustworthy3. References: ISO
/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor Training Course - BSI
Question 94
您正在一家提供醫療保健服務的住宅療養院進行 ISMS 審核。審核計畫的下一步是驗證資訊安全事件管理流程。 IT 安全經理提出了資訊安全事件管理程序(文件參考 ID:ISMS_L2_16,版本 4)。
您查看該文件並注意到一條聲明「任何資訊安全弱點、事件和事故應在識別後 1 小時內報告給聯絡人 (PoC)」。在訪問員工時,您發現大家對「弱點、事件、事件」這幾個詞的含義理解有差異。
IT安全經理解釋說,6個月前舉辦了一次線上「資訊安全應對」培訓研討會。所有受訪的人都參加並通過了報告練習和課程評估。
您想進一步調查其他領域以收集更多審計證據。選擇三個不是有效審計追蹤的選項。
您查看該文件並注意到一條聲明「任何資訊安全弱點、事件和事故應在識別後 1 小時內報告給聯絡人 (PoC)」。在訪問員工時,您發現大家對「弱點、事件、事件」這幾個詞的含義理解有差異。
IT安全經理解釋說,6個月前舉辦了一次線上「資訊安全應對」培訓研討會。所有受訪的人都參加並通過了報告練習和課程評估。
您想進一步調查其他領域以收集更多審計證據。選擇三個不是有效審計追蹤的選項。
Correct Answer: E,G,H
The three options that would not be valid audit trails are:
*Collect more evidence on how the organisation manages the Point of Contact (PoC) which monitors vulnerabilities. (Relevant to clause 8.1)
*Collect more evidence on whether terms and definitions are contained in the information security policy.
(Relevant to control 5.32)
*Collect more evidence to determine if ISO 27035 (Information security incident management) is used as internal audit criteria. (Relevant to clause 8.13) These options are not valid audit trails because they are not directly related to the information security incident management process, which is the focus of the audit. The audit trails should be relevant to the objectives, scope, and criteria of the audit, and should provide sufficient and reliable evidence to support the audit findings and conclusions1.
Option E is not valid because the PoC is not a part of the information security incident management process, but rather a role that is responsible for reporting and escalating information security incidents to the appropriate authorities2. The audit trail should focus on how the PoC performs this function, not how the organisation manages the PoC.
Option G is not valid because the terms and definitions are not a part of the information security incident management process, but rather a part of the information security policy, which is a high-level document that defines the organisation's information security objectives, principles, and responsibilities3. The audit trail should focus on how the information security policy is communicated, implemented, and reviewed, not whether it contains terms and definitions.
Option H is not valid because ISO 27035 is not a part of the information security incident management process, but rather a guidance document that provides best practices for managing information security incidents4. The audit trail should focus on how the organisation follows the requirements of ISO/IEC 27001:
2022 for information security incident management, not whether it uses ISO 27035 as an internal audit criteria.
The other options are valid audit trails because they are related to the information security incident management process, and they can provide useful evidence to evaluate the conformity and effectiveness of the process. For example:
*Option A is valid because it relates to control A.5.29, which requires the organisation to establish procedures to isolate and quarantine areas subject to information security incidents, in order to prevent further damage and preserve evidence5. The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation implements and tests these procedures, and how they ensure the continuity of information security during disruption.
*Option B is valid because it relates to control A.6.8, which requires the organisation to establish mechanisms for reporting information security events and weaknesses, and to ensure that they are communicated in a timely manner to the appropriate levels within the organisation6. The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation defines and uses these mechanisms, and how they monitor and review the reporting process.
*Option C is valid because it relates to clause 7.2, which requires the organisation to provide information security awareness, education, and training to all persons under its control, and to evaluate the effectiveness of these activities7. The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation identifies the information security training needs, how they deliver and record the training, and how they measure the learning outcomes and feedback.
*Option D is valid because it relates to control A.5.27, which requires the organisation to learn from information security incidents and to implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence or reduce impact8.
The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation analyses and documents the root causes and consequences of information security incidents, how they identify and implement corrective actions, and how they verify the effectiveness of these actions.
*Option F is valid because it relates to control A.5.30, which requires the organisation to establish and maintain a business continuity plan to ensure the availability of information and information processing facilities in the event of a severe information security incident9. The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation develops and updates the business continuity plan, how they test and review the plan, and how they communicate and train the relevant personnel on the plan.
References: 1: ISO 19011:2018, 6.2;
2: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.6.8.1;
3: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, 5.2;
4: ISO/IEC 27035:2016, Introduction;
5: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.5.29;
6: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.6.8;
7: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, 7.2;
8: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.5.27;
9: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.5.30;
10: ISO 19011:2018;
11: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
12: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
13: ISO/IEC 27035:2016;
14: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
15: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
16: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
17: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
18: ISO/IEC 27001:2022
*Collect more evidence on how the organisation manages the Point of Contact (PoC) which monitors vulnerabilities. (Relevant to clause 8.1)
*Collect more evidence on whether terms and definitions are contained in the information security policy.
(Relevant to control 5.32)
*Collect more evidence to determine if ISO 27035 (Information security incident management) is used as internal audit criteria. (Relevant to clause 8.13) These options are not valid audit trails because they are not directly related to the information security incident management process, which is the focus of the audit. The audit trails should be relevant to the objectives, scope, and criteria of the audit, and should provide sufficient and reliable evidence to support the audit findings and conclusions1.
Option E is not valid because the PoC is not a part of the information security incident management process, but rather a role that is responsible for reporting and escalating information security incidents to the appropriate authorities2. The audit trail should focus on how the PoC performs this function, not how the organisation manages the PoC.
Option G is not valid because the terms and definitions are not a part of the information security incident management process, but rather a part of the information security policy, which is a high-level document that defines the organisation's information security objectives, principles, and responsibilities3. The audit trail should focus on how the information security policy is communicated, implemented, and reviewed, not whether it contains terms and definitions.
Option H is not valid because ISO 27035 is not a part of the information security incident management process, but rather a guidance document that provides best practices for managing information security incidents4. The audit trail should focus on how the organisation follows the requirements of ISO/IEC 27001:
2022 for information security incident management, not whether it uses ISO 27035 as an internal audit criteria.
The other options are valid audit trails because they are related to the information security incident management process, and they can provide useful evidence to evaluate the conformity and effectiveness of the process. For example:
*Option A is valid because it relates to control A.5.29, which requires the organisation to establish procedures to isolate and quarantine areas subject to information security incidents, in order to prevent further damage and preserve evidence5. The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation implements and tests these procedures, and how they ensure the continuity of information security during disruption.
*Option B is valid because it relates to control A.6.8, which requires the organisation to establish mechanisms for reporting information security events and weaknesses, and to ensure that they are communicated in a timely manner to the appropriate levels within the organisation6. The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation defines and uses these mechanisms, and how they monitor and review the reporting process.
*Option C is valid because it relates to clause 7.2, which requires the organisation to provide information security awareness, education, and training to all persons under its control, and to evaluate the effectiveness of these activities7. The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation identifies the information security training needs, how they deliver and record the training, and how they measure the learning outcomes and feedback.
*Option D is valid because it relates to control A.5.27, which requires the organisation to learn from information security incidents and to implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence or reduce impact8.
The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation analyses and documents the root causes and consequences of information security incidents, how they identify and implement corrective actions, and how they verify the effectiveness of these actions.
*Option F is valid because it relates to control A.5.30, which requires the organisation to establish and maintain a business continuity plan to ensure the availability of information and information processing facilities in the event of a severe information security incident9. The audit trail should collect evidence on how the organisation develops and updates the business continuity plan, how they test and review the plan, and how they communicate and train the relevant personnel on the plan.
References: 1: ISO 19011:2018, 6.2;
2: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.6.8.1;
3: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, 5.2;
4: ISO/IEC 27035:2016, Introduction;
5: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.5.29;
6: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.6.8;
7: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, 7.2;
8: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.5.27;
9: ISO/IEC 27001:2022, A.5.30;
10: ISO 19011:2018;
11: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
12: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
13: ISO/IEC 27035:2016;
14: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
15: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
16: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
17: ISO/IEC 27001:2022;
18: ISO/IEC 27001:2022
Question 95
ISMS的標準定義是什麼?
Correct Answer: D
The standard definition of ISMS is a systematic approach for establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining and improving an organization's information security to achieve business objectives. This definition is given in clause 3.17 of ISO/IEC 27001:2022, and it describes the main components and purpose of an ISMS. An ISMS is not a project-based approach, as it is an ongoing process that requires continual improvement. An ISMS is not a company wide business objective, as it is a management system that supports the organization's objectives. An ISMS is not an information security systematic approach, as it is a broader concept that encompasses the organization's context, risks, controls, and performance. Reference: : CQI & IRCA ISO 27001:2022 Lead Auditor Course Handbook, page 15. : ISO/IEC 27001:2022, clause 3.17.
- Latest Upload
- 155Fortinet.FCP_FAZ_AD-7.4.v2026-01-16.q115
- 177PECB.ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Auditor-CN.v2026-01-16.q166
- 130Talend.Talend-Core-Developer.v2026-01-15.q20
- 179Salesforce.Marketing-Cloud-Administrator.v2026-01-15.q146
- 245Salesforce.ADX-211.v2026-01-14.q223
- 137Salesforce.B2B-Solution-Architect.v2026-01-14.q111
- 143BICSI.RCDD.v2026-01-14.q121
- 131NBMTM.BCMTMS.v2026-01-14.q33
- 132Microsoft.GH-200.v2026-01-13.q64
- 151SAP.C_C4HCX_2405.v2026-01-13.q80
[×]
Download PDF File
Enter your email address to download PECB.ISO-IEC-27001-Lead-Auditor-CN.v2026-01-16.q166 Practice Test

