Question 31
Which THREE of the following are advantages of activity-based costing (ABC), in a multi-product environment, when compared with traditional absorption costing?
Question 32
A company has budgeted to produce 5,000 units of Product B per month. The opening and closing inventories of Product B for next month are budgeted to be 400 units and 900 units respectively. The budgeted selling price and variable production costs per unit for Product B are as follows:

Total budgeted fixed production overheads are $29,500 per month.
The company absorbs fixed production overheads on the basis of the budgeted number of units produced. The budgeted profit for Product B for next month, using absorption costing, is $20,700.
Prepare a marginal costing statement which shows the budgeted profit for Product B for next month.
What was the marginal costing profit for the next month?

Total budgeted fixed production overheads are $29,500 per month.
The company absorbs fixed production overheads on the basis of the budgeted number of units produced. The budgeted profit for Product B for next month, using absorption costing, is $20,700.
Prepare a marginal costing statement which shows the budgeted profit for Product B for next month.
What was the marginal costing profit for the next month?
Question 33
A company produces trays of pre-prepared meals that are sold to restaurants and food retailers. Three varieties of meals are sold: economy, premium and deluxe.
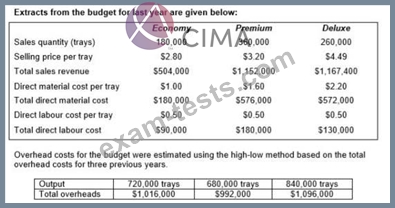
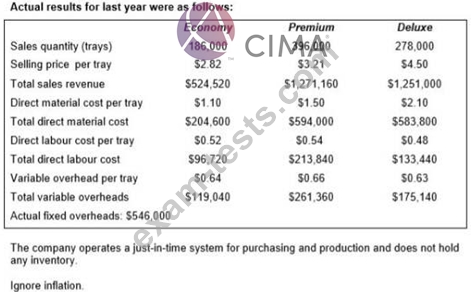
Calculate, for the original budget, the budgeted fixed overhead costs, the budgeted variable overhead cost per tray and the budgeted total overheads costs.


Calculate, for the original budget, the budgeted fixed overhead costs, the budgeted variable overhead cost per tray and the budgeted total overheads costs.
Question 34
For the forthcoming period, the number of units of product L produced must be no more than four times the number of units of product M produced.
The equation to represent this constraint in a linear programming exercise is:
The equation to represent this constraint in a linear programming exercise is:
Question 35
A company makes a product using two materials, X and Y.
The standard materials required for one unit of the product are:

What is the direct material mix variance for Material X, using the individual valuation basis?
The standard materials required for one unit of the product are:

What is the direct material mix variance for Material X, using the individual valuation basis?

