Question 51
The cost card for one unit of Product G is as follows:
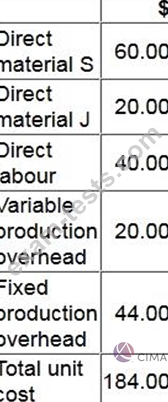
The opening and closing inventories of Product G for month 5 are budgeted to be 10 units and 60 units respectively.
Profit for month 5 using absorption costing is budgeted to be $15,000.
What is the budgeted profit for month 5 using throughput costing?

The opening and closing inventories of Product G for month 5 are budgeted to be 10 units and 60 units respectively.
Profit for month 5 using absorption costing is budgeted to be $15,000.
What is the budgeted profit for month 5 using throughput costing?
Question 52
Company X is deciding which of Projects A, B or C to undertake. The profit earned from each of the projects is dependent on economic conditions.
The table below details the profit for each of the possible outcomes and the expected value of each of the projects.
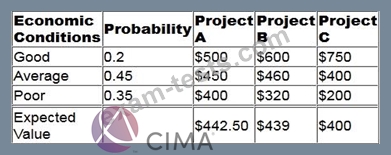
What is the maximum amount that should be paid for perfect information about the economic conditions?
The table below details the profit for each of the possible outcomes and the expected value of each of the projects.

What is the maximum amount that should be paid for perfect information about the economic conditions?
Question 53
A company sells three products A, B and C in a ratio of 2:2:3.
Each unit of A,B and C earns a contribution of $4.00, $2.00 and $4.00 respectively. Production fixed costs are $69,000 each month and selling fixed costs are $13,000 each month.
The company holds no inventory. The management accountant wants to know the total number of units needed to break-even. However, he is unsure about how to calculate the weighted average contribution per unit or what category of fixed cost to use.
Place the amounts given to complete the table in order to calculate the total number of units to break even.
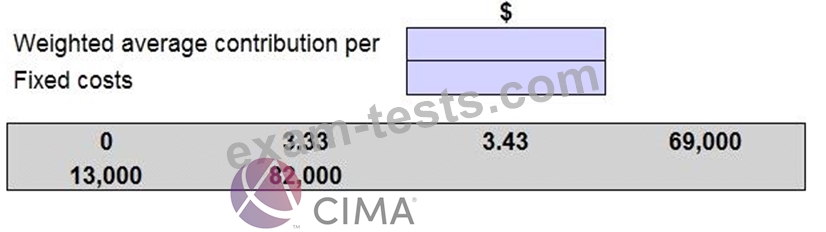
Each unit of A,B and C earns a contribution of $4.00, $2.00 and $4.00 respectively. Production fixed costs are $69,000 each month and selling fixed costs are $13,000 each month.
The company holds no inventory. The management accountant wants to know the total number of units needed to break-even. However, he is unsure about how to calculate the weighted average contribution per unit or what category of fixed cost to use.
Place the amounts given to complete the table in order to calculate the total number of units to break even.

Question 54
A company is considering the use of Material V in a special order.
The material is used regularly and a sufficient quantity of the material is in inventory.
It could also be sold, at just below the current market price, to a local competitor.
What is the relevant cost of Material V to be used in the special contract?
The material is used regularly and a sufficient quantity of the material is in inventory.
It could also be sold, at just below the current market price, to a local competitor.
What is the relevant cost of Material V to be used in the special contract?
Question 55
A major company sells a range of electrical, clothing and homeware products through a chain of department stores. The main administration functions are provided from the company's head office. Each department store has its own warehouse which receives goods that are delivered from a central distribution center.
The company currently measures profitability by product group for each store using an absorption costing system. All overhead costs are charged to product groups based on sales revenue. Overhead costs account for approximately one-third of total costs and the directors are concerned about the arbitrary nature of the current method used to charge these costs to product groups.
A consultant has been appointed to analyses the activities that are undertaken in the department stores and to establish an activity based costing system.
The consultant has identified the following data for the latest period for each of the product groups for the X Town store:
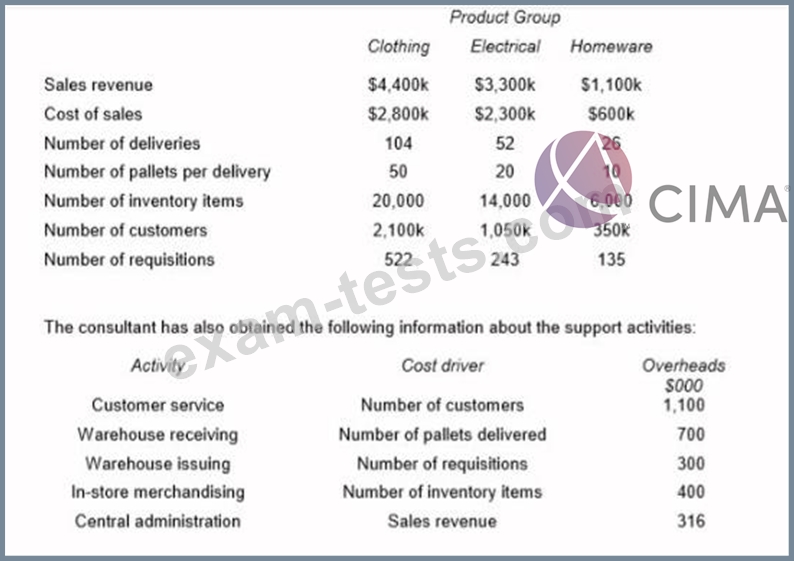
Calculate the total profit for each of the product groups:
.... using the current absorption costing system;
The company currently measures profitability by product group for each store using an absorption costing system. All overhead costs are charged to product groups based on sales revenue. Overhead costs account for approximately one-third of total costs and the directors are concerned about the arbitrary nature of the current method used to charge these costs to product groups.
A consultant has been appointed to analyses the activities that are undertaken in the department stores and to establish an activity based costing system.
The consultant has identified the following data for the latest period for each of the product groups for the X Town store:

Calculate the total profit for each of the product groups:
.... using the current absorption costing system;


