Question 56
A company is considering hedging the interest rate risk on a 3-year floating rate borrowing linked to the 12-month risk-free rate.
If the 12-month risk-free rate for the next three years is 2%, 3% and 4%, which of the following alternatives would result in the lowest average finance cost for the company over the three years?
If the 12-month risk-free rate for the next three years is 2%, 3% and 4%, which of the following alternatives would result in the lowest average finance cost for the company over the three years?
Question 57
An unlisted software development business is to be sold by its founders to a private equity house following the initial development of the software. The business has not yet made a profit but significant profits are expected for the next three years with only negligible profits thereafter. The business owns the freehold of the property from which it operates. However, it is the industry norm to lease property.
Which THREE of the following are limitations to the validity of using the Calculated Intangible Value (CIV) method for this business?
Which THREE of the following are limitations to the validity of using the Calculated Intangible Value (CIV) method for this business?
Question 58
A company is currently all-equity financed with a cost of equity of 8%.
It plans to raise debt with a pre-tax cost of 4% in order to buy back equity shares.
After the buy-back, the debt-to-equity ratio at market values will be 1 to 2.
The corporate income tax rate is 30%.
Which of the following represents the company's cost of equity after the buy-back according to Modigliani and Miller's Theory of Capital Structure with taxes?
It plans to raise debt with a pre-tax cost of 4% in order to buy back equity shares.
After the buy-back, the debt-to-equity ratio at market values will be 1 to 2.
The corporate income tax rate is 30%.
Which of the following represents the company's cost of equity after the buy-back according to Modigliani and Miller's Theory of Capital Structure with taxes?
Question 59
Company A has made an offer to take over all the shares in Company B on the following terms:
* For every 20 shares currently held, Company B's shareholders will receive $100 bond with a coupon rate of 3%
* The bond will be repaid in 10 years' time at its par value of $100.
* The current yield on 10 year bonds of similar risk is 6%.
What is the effective offer price per share being made to Company B's shareholders?
* For every 20 shares currently held, Company B's shareholders will receive $100 bond with a coupon rate of 3%
* The bond will be repaid in 10 years' time at its par value of $100.
* The current yield on 10 year bonds of similar risk is 6%.
What is the effective offer price per share being made to Company B's shareholders?
Question 60
Company HJK is planning to bid for listed company BNM
Financial data for BNM for the financial year ended 31 December 20X1:
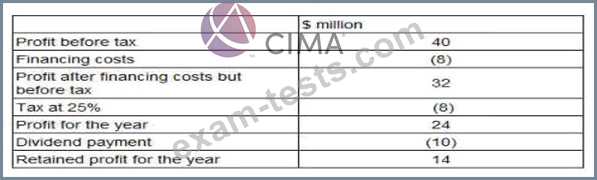
HJK is not forecasting any growth in these figures for the foreseeable future
Profit and cost data above should be assumed to be equivalent to cash flow data when answenng this question
Which THREE of the following approaches would be most appropriate for HJK to use to value the equity of BNM?
Financial data for BNM for the financial year ended 31 December 20X1:

HJK is not forecasting any growth in these figures for the foreseeable future
Profit and cost data above should be assumed to be equivalent to cash flow data when answenng this question
Which THREE of the following approaches would be most appropriate for HJK to use to value the equity of BNM?

